- AI Collections @Beehiiv
- Posts
- From Chatbots to Chipmakers: Generative AI's Impact on Stock Market
From Chatbots to Chipmakers: Generative AI's Impact on Stock Market
Discover the secret AI Strategies of Tech Giants: Apple, Amazon, Google, Meta, Microsoft, and Nvidia.
The AI landscape is transforming not just technology but also the stock market dynamics. After ChatGPT became hugely popular, generative AI has picked up interest and adoption from people at a large scale, and the sentiments around AI have significantly driven the stock prices of AI companies to new levels in the past few months.
Companies are investing billions of dollars to ramp up innovation and production in AI, releasing products almost every day.
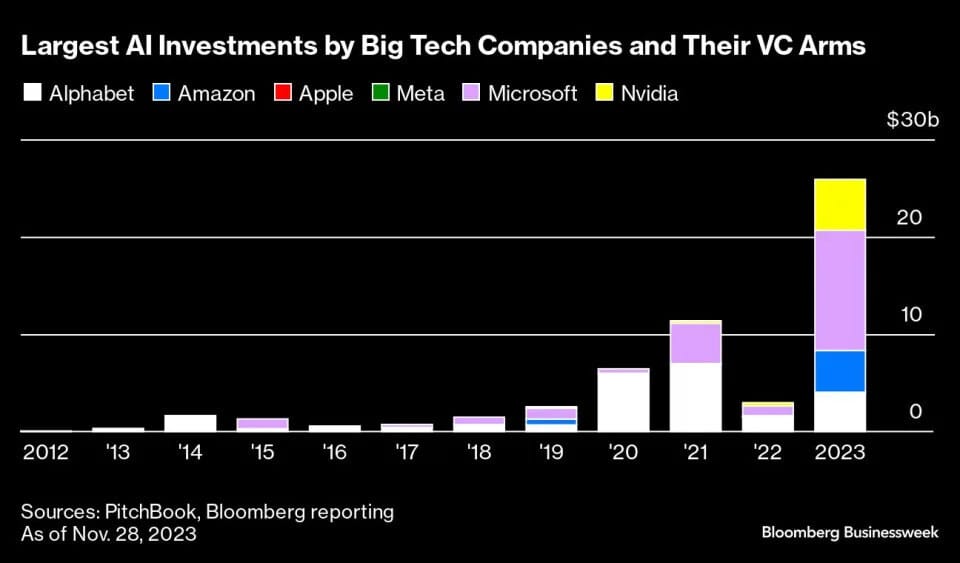
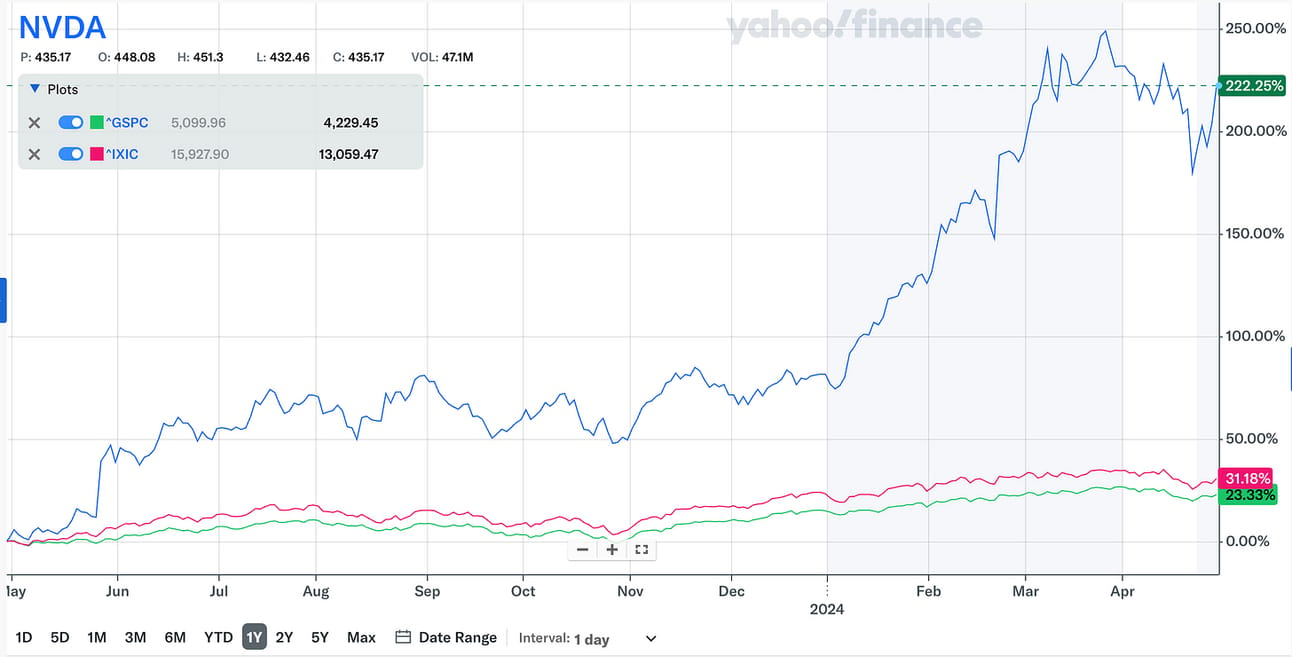
The S&P 500 index clocked a growth of almost 25% from October to April 2024, touching its highest-ever point. The tech behemoth Nvidia led the market which itself grew by over 117% till March 2024, contributing the most to the returns of these indexes. So much so that some investors are now whispering “bubble” that is expected to burst. What followed this trend was a heightened fear of correction and significant volatility in the market.
This has left investors like us in a dilemma: what to expect? Is the sentiment for generative AI declining? Should we invest more in the sector or not?
We felt bringing the facts to the table would help clear out some confusion, giving a better picture of what to expect and decide the future course of action.
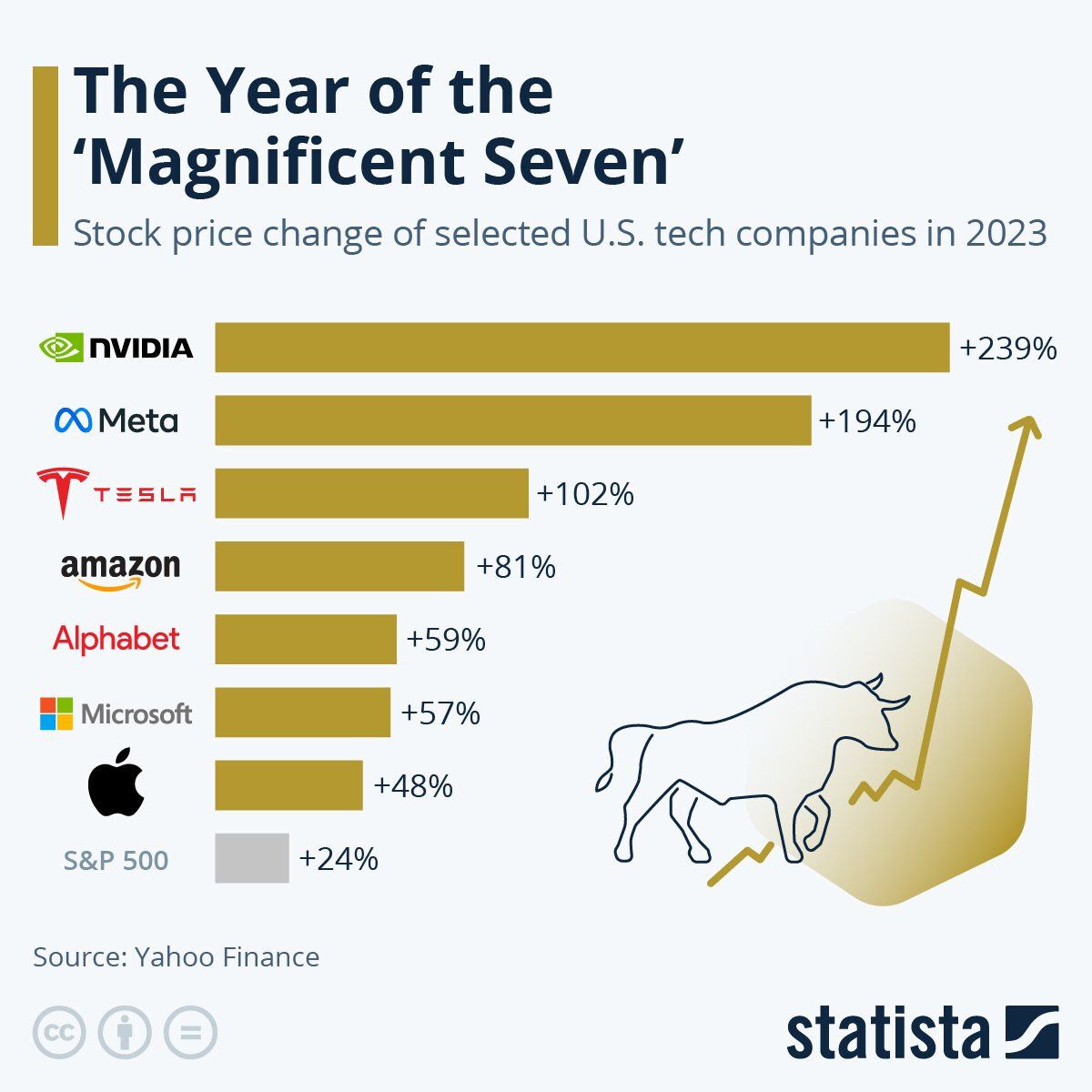
In this blog, we are focusing on the Magnificent 7 stocks: Apple, Alphabet, Microsoft, Amazon, Nvidia, Tesla, and Meta, which are leading the charge in AI. We will present how market factors like inflation, interest rates, geopolitics, and other factors are broadly affecting the industry, and then dive into company-specific macro factors. By the end of the blog, we will briefly overview the facts and understand how to navigate this market for taking informed actions.
Why Magnificent 7?
The Magnificent 7, through their sheer size and influence, are more than just market participants; they are trendsetters whose technological innovations and financial performances set the pace for the broader market. Their stock prices reflect the market sentiment and investor confidence in tech.
These companies alone contribute to around 30% of the S&P500 index. Microsoft, with the largest weighting among them, followed by Apple and Nvidia, has a significant impact on the index's movements. Any substantial price movement in these stocks can lead to notable index-level changes, which illustrates the extent to which these giants can steer market direction.
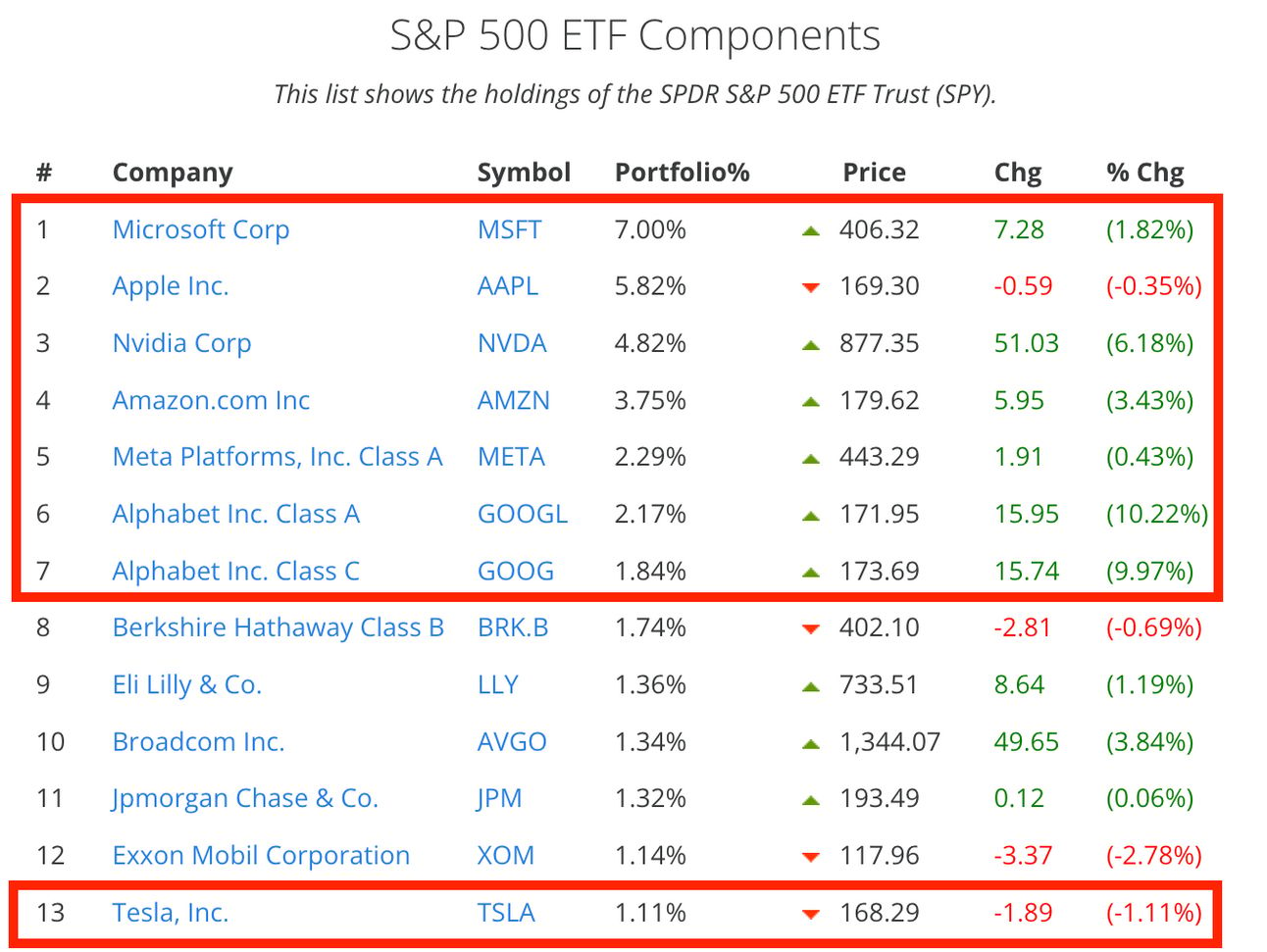
Nvidia’s market cap touched $2 trillion last month, with returns contributing almost 1/3rd to the gains alone in the S&P500 index. (Source). The index gained 7% year-to-date, 6% out of which was contributed by just 4 companies: Nvidia, Meta, Amazon, and Microsoft. (Source)
It’s quite clear now that the movement in these 7 titans mirrors the pulse of the market. As the technological landscape evolves, so too does the influence of these heavyweights on the market.
But these companies don’t function in isolation. A range of factors affect the industry like inflation, interest rates, and geopolitics. Let’s zoom into these vitals and understand how these interplay to influence the AI and tech industry at large.
Broad factors affecting the industry
1. Inflation and Interest rate
High inflation rapidly erodes purchasing power and adds a layer of uncertainty for businesses, impacting their cost estimations and investment capabilities. For the AI industry, this means increased operational and development costs which could slow down the pace of innovation and product rollout.
To curb inflation, the central bank increases the interest rate that makes the scenario more complicated. The borrowing cost increases, and for AI companies, particularly those reliant on external financing, this dampens the investment in new projects or research.
The annual inflation rate in the United States for the last 12 months was 3.5%, a slight uptick from the previous 3.2% (source). While this rate has seen a decrease from the peak in June 2022, it remains above the Federal Reserve’s target of 2%.
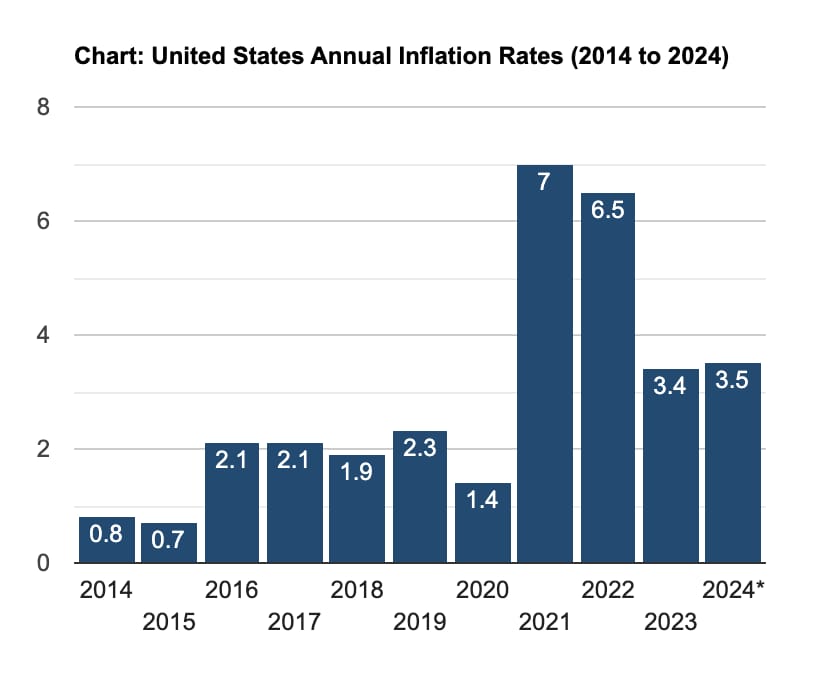
The market expected the Fed to ease the rate but it left rates unchanged in its latest meeting (source), considering the inflation numbers. Some experts say that the Fed might not decrease the interest rate at all in 2024 (source), spurring uncertainty among investors. This implies continued headwinds for the market in general, including the tech industry.
2. Govt’s spending and initiatives to grow the industry
The government’s outlook towards the industry is one of the major influencers. This can be seen from the investments the government plans to make for the industry’s growth and the regulations around it.
The US government’s increased budget for AI spending signals the potential it sees in the technology. The 2025 federal budget has earmarked substantial funds of $3 billion to develop, test, procure, and integrate AI across federal operations, and $300 million “in mandatory funding to increase agency funding for AI.” The budget also includes $70 million for agencies to create chief AI officers accountable for their agency’s use of AI. (Source)
The Administration also released an Executive Order in October 2023 to promote the responsible use of AI and harness the benefits of this groundbreaking technology (Source). While one might say that these regulations curb the innovation and adoption in the field, these initiatives actually instill confidence that the government believes and acknowledges the potential as well as risks of AI, as it lays down a clear roadmap for AI’s integration more widely, reflecting on the performance and valuations of AI-focused companies.

3. Sector valuations
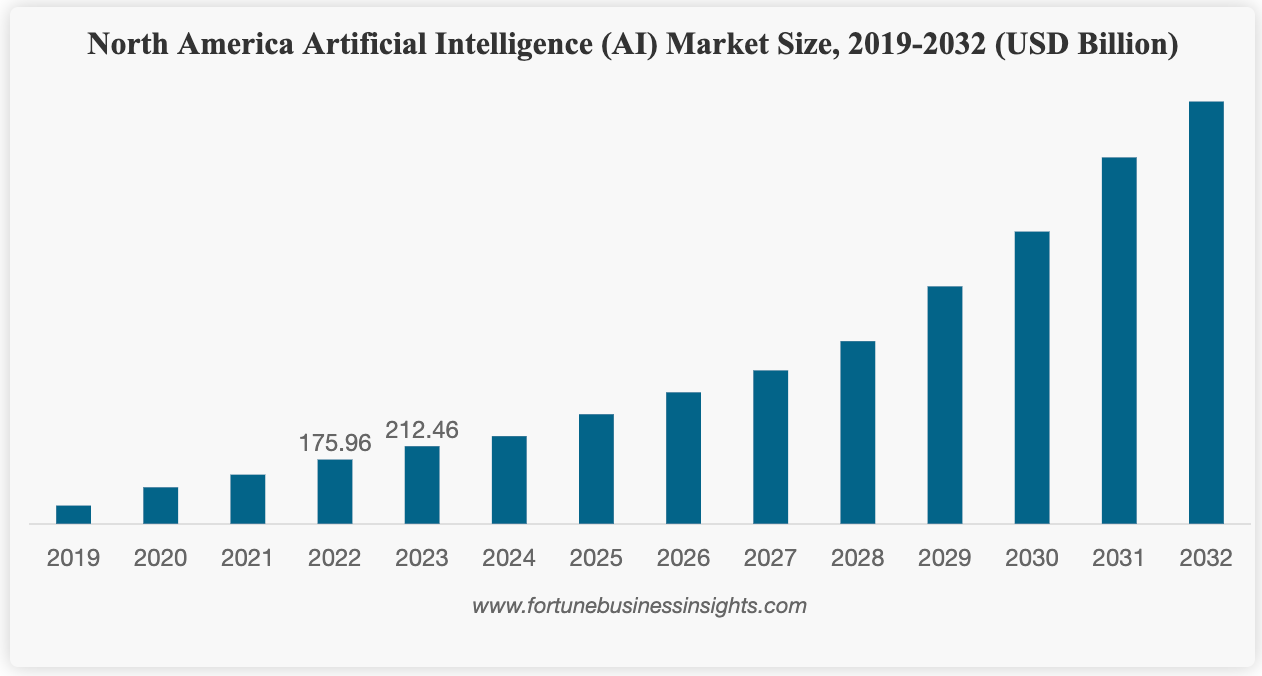
Sector valuations are crucial in assessing the financial health and growth prospects of industries, including AI. The AI market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating that its value will escalate from $621.19 billion in 2024 to $2,740.46 billion by 2032, a compound annual growth rate of 20.4% during this period. North America, buoyed by industry leaders like IBM, Microsoft, and Nvidia, dominates this market space.
Such promising figures suggest a vibrant investment landscape for AI, where advancements in technology and rising adoption in various sectors fuel market confidence and attract investor interest. This expansion is not just confined to the tech giants but is also seen in startups and SMEs integrating AI into their service operations for improved efficiency and customer service. (Source)
4. Market sentiment for tech and AI
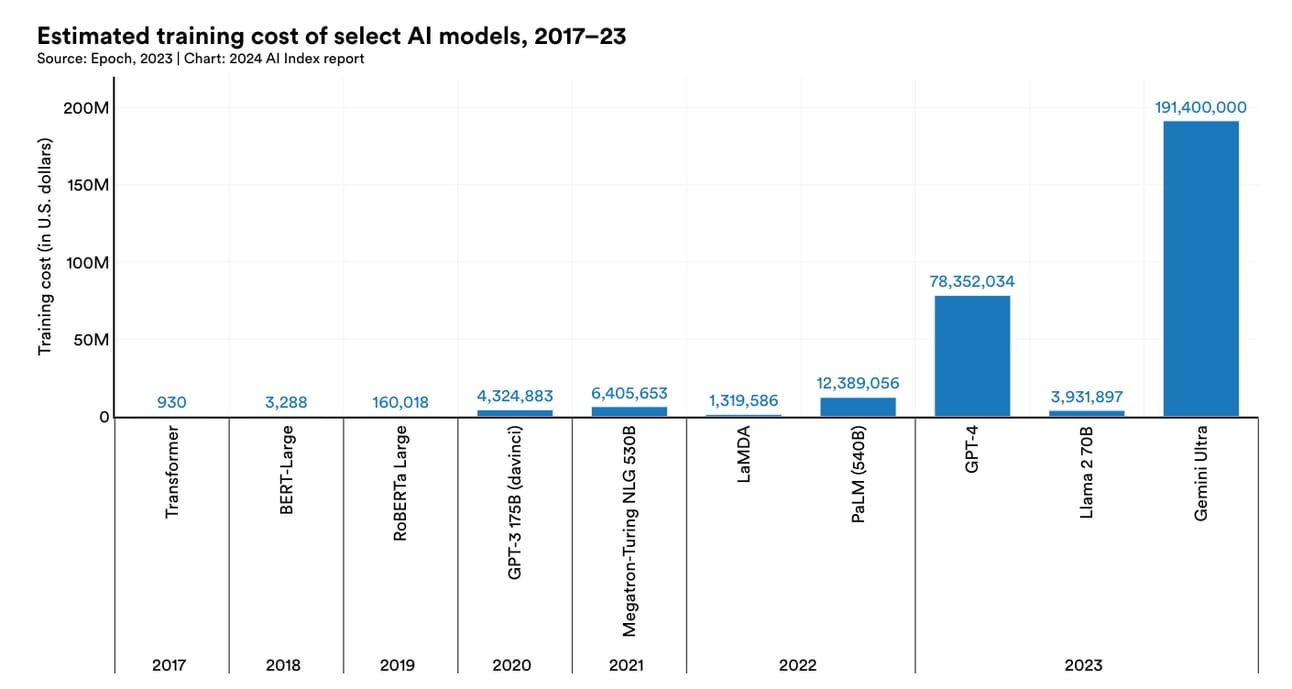
The post-ChatGPT era has uplifted the market sentiments significantly. But this is coupled with substantial caution considering the increased mishaps of data leaks, deepfakes, and misinformation. Technical breakthroughs, like the excellent performance demonstrated by the new Gemini models or Meta’s Llama 3 are turning heads and opening wallets, with investments in generative AI hitting a staggering $25.2 billion last year. But it’s not without its hurdles. The sheer cost of developing these advanced models is astronomical, like Google flaunting a spend of $191 million on Gemini, edging out the smaller players, and shaping a market dominated by the big guns (Sources: Deloitte, Stanford).
The excitement is also tempered by growing concerns about the ethical use of AI. Public sentiment is shifting too; more people are starting to feel uneasy about AI. This nervous backdrop is compounded by a lack of transparency from AI developers, leaving many to wonder about what's going on under the hood.
Despite these challenges, the financial upside of AI adoption is evident, with many firms reporting cost savings and revenue boosts. Big names like Microsoft, Nvidia, and Apple are betting big on AI, weaving it into everything from cloud services to autonomous vehicles. This deep integration promises to rev up their growth engines.
5. Geopolitics
Geopolitical events are casting a long-lasting shadow over the AI landscape, influencing how and where technologies develop and who controls them. At the heart of this drama are the U.S. and China, whose rivalry in AI technology is intensifying. With companies like the Magnificent 7 and Qualcomm in the US and Baidu, Alibaba, or Tencent in China, both nations are pumping vast sums into AI, but their competition is making technology sharing and collaboration a casualty. (Source)
The U.S. is playing a “Small Yard, High Fence” game, using export controls to limit China’s access to critical semiconductors necessary for AI systems and this strategy is reciprocated by China. The situation has led to fractured technical blocs with parallel development of overlapping technologies, coupled with export controls and restricted market access which makes it complex for companies to navigate the international markets. For instance, Tesla is facing a significant challenge in penetrating the Chinese EV market where stringent controls and favoritism towards local companies like BYD, affecting the company’s sales. (Source)
A pivotal player in this geopolitical drama is Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), the world’s leading producer of advanced semiconductors. The geopolitical tension surrounding Taiwan, along with TSMC's central position makes global AI development vulnerable to regional instability. (Source)
This splintering is seen across multiple fronts. For instance, the UK, Saudi Arabia, and India are also vying to carve out their niches in AI, each adopting different strategies to foster innovation or secure technologies.
The situation has also been exaggerated by the recent attacks and tensions in the Middle East involving Israel and Iran, which has heightened the uncertainty about global stability and oil supply disruptions, hitting the US stock market broadly.
AI Growth vs the .com Bubble
The growth in AI companies, specifically Nvidia, has led many investors and analysts to factor in the possibility of hitting a bubble, similar to the .com bubble of the early 2000s. Instead of making mere speculations based solely on the growth of one company, it’s better to focus on some numbers and facts to assert if we are at the peak already.
Market Multiples: At the peak of the .com bubble in 2000, Nasdaq traded at an absurdly high price to earnings ratio (P/E) of 200, driven by companies like Cisco and Qualcomm (source). This is extremely high in comparison to the P/E of tech companies today, with Nvidia’s being the most at 100.96 and Apple at 26.37. The P/E of the S&P500 ETF by iShares stood 25.36, and Nasdaq ETF by Invest P/E is 33.81.
Returns: Nasdaq 100 was on fire in the late 1990s! The four-year rolling return from 1995-1999 was nearly 700% at the dot-com peak. Today, the Nasdaq 100 has seen four-year rolling returns of about 100%. (Source)
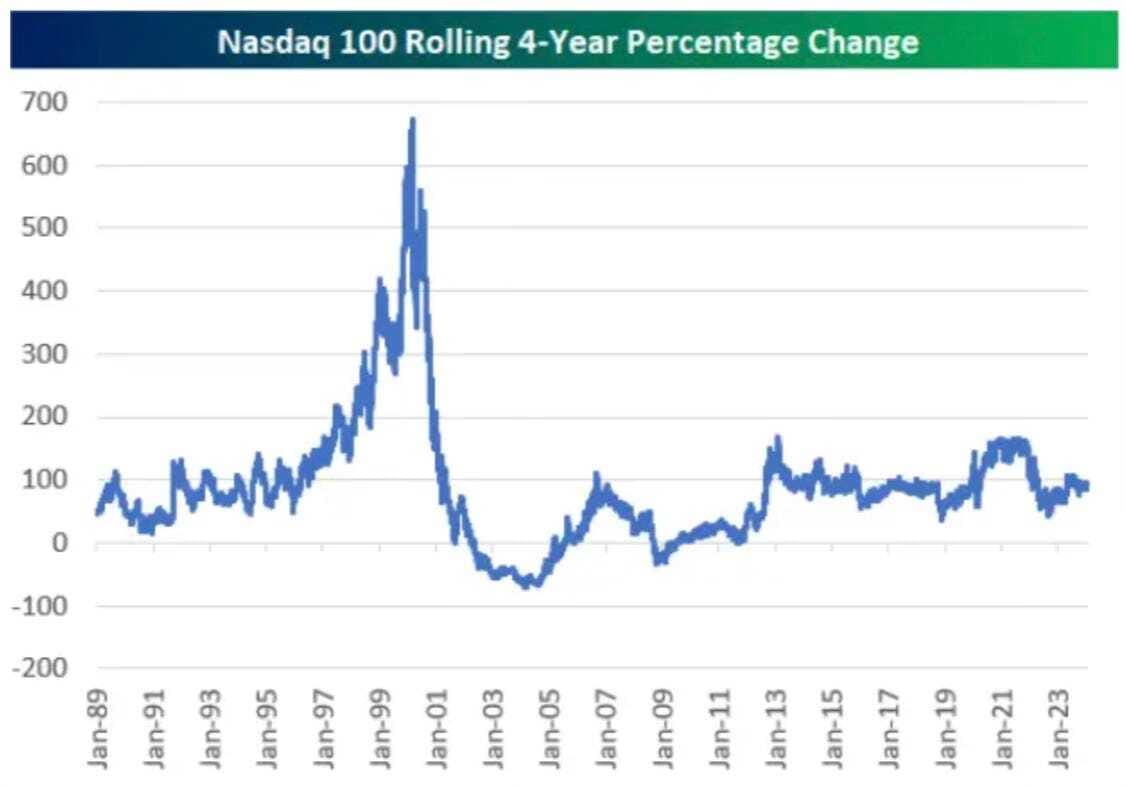
The concentration of market capitalization among top tech companies mirrors the late 1990s, yet today’s leading companies demonstrate a stronger foundation in actual earnings and technological integration. The AI-driven rally is supported by real-world applications and innovations in AI, for instance, Nvidia’s new Blackwell platform, Meta’s state-of-the-art new opensource Llama 3 models, Google’s Gemini models, Tesla’s innovation in the autonomous driving technology, and much more!
These innovations justify their market premiums, much more than the internet prospects did in the 1990s. The investor behavior also reflects this shift; the speculative fervor of the .com era has been replaced by a more measured enthusiasm for AI stocks. Reminiscing the previous bubble, the market today is more cautious about potential overvaluation.
Now that we’ve understood the broad factors affecting the industry, it’s time to dive into the specifics of each of the Magnificent 7.
Apple
Brief Summary of the Business
Apple is known for its extensive range of consumer electronics, including iPhones, iPads, Mac computers, Apple Watch and other devices like AirPods and Vision Pro, along with its software ecosystems powered by iOS, macOS, and watchOS. The company's innovation extends into services like Apple Music, iCloud, and the App Store, making it a comprehensive hub for technology solutions.
AI Integration and Innovation
Apple has been one of the earliest movers is using AI with its assistant Siri and facial recognition, and over the year has been deepening AI integration across its product line. One of the standout developments is Apple Vision Pro, a device that epitomizes Apple’s push into using AI for more immersive and interactive technology experiences.

Apple has been facing criticism lately for “lagging behind” in the generative AI race in comparison to peers like Google and Microsoft who have released their state-of-the-art LLMs powering the new-age AI chatbots. But Apple is known to keep its innovations under the wrap and release showcase them directly in its products.
On the research front, Apple has released some updates, for instance, a detailed report on its multimodal AI models which might power its next generation of AI capabilities, another multimodal LLM that can understand spatial reference in an image, the MLX framework for machine learning research on Apple’s devices, and ReALM models that can understand and successfully handle context of different kinds.
The company’s WWDC 2024 event is also expected to showcase a range of generative AI capabilities running on-device. The upcoming M4 chips will reportedly boost AI performance, tailored specifically to enhance AI and machine learning tasks directly on Apple devices. Siri is expected to get more intuitive and helpful, integrating more deeply with other native apps and services. Apple is also exploring personal robotics as a new area for innovation and revenue generation.

The strategy is not just about catching up with current AI trends but integrating AI into the daily digital experiences of its users.
Financial Performance
In the first quarter of fiscal year 2024, Apple reported a revenue of $119.6 billion, marking a modest 2% increase from the previous year, and a significant earnings per share increase of 16% to $2.18. These figures show Apple’s robust operational efficiency despite the competitive market. The company’s performance was particularly bolstered by strong iPhone sales and record-setting revenue from its services sector. (source)
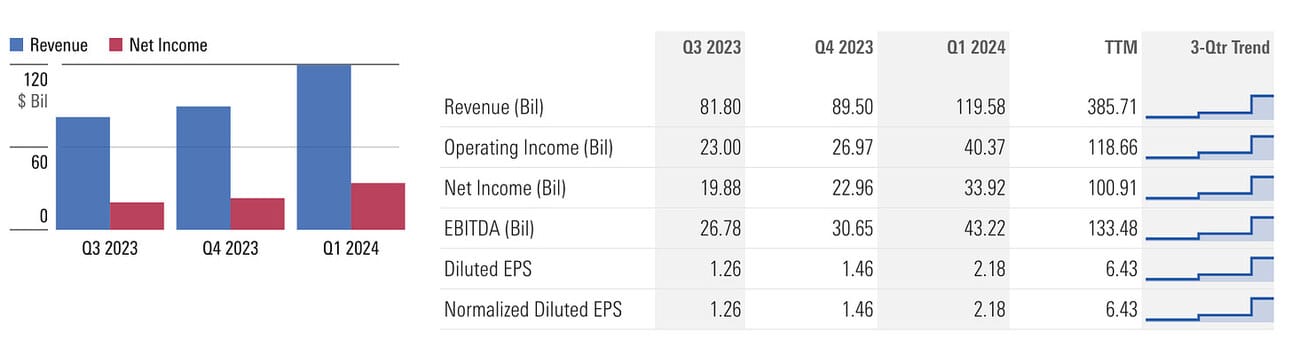
Apple also reported a strong operational cash flow of nearly $40 billion during the quarter, which shows strong financial management and the ability to fund its ambitious growth plans, including further investments in AI technologies. The strategic focus in services and wearables has made it successful for the company to generate revenue from diverse streams.
Although overall revenue increased, specific segments like iPad and the Wearables, Home, and Accessories category saw declines. iPad revenue was down 25% year-over-year, and Wearables also declined by 11%. It is important to know here that a significant portion of Apple’s revenue is heavily reliant on its flagship products, particularly the iPhone. Any missteps in product upgrades or technological advancements can significantly impact overall revenue.
Operational Efficiencies
Along with a robust revenue and EPS, Apple also has a strong gross and net profit margin of 45.87% and 35.16%. The return on assets and equity reflect an efficient use assets and equity to generate earnings and profits. The strong cash flow and liquidity also show Apple’s strengths in operational efficiencies.
However, being out of Apple’s control, there have been supply chain issues due to ongoing bottlenecks and power restrictions in China, where most of its manufacturing partners like Foxconn and Pegatron are located. These challenges have led to decreased production rates, especially during periods traditionally marked by ramped-up activity to meet holiday demand.
Further, the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) has filed a major antitrust lawsuit against Apple, accusing the company of monopolistic practices in the app ecosystem, claiming that Apple imposes restrictions that stifle competition and maintain its monopoly power in the smartphone and related markets.
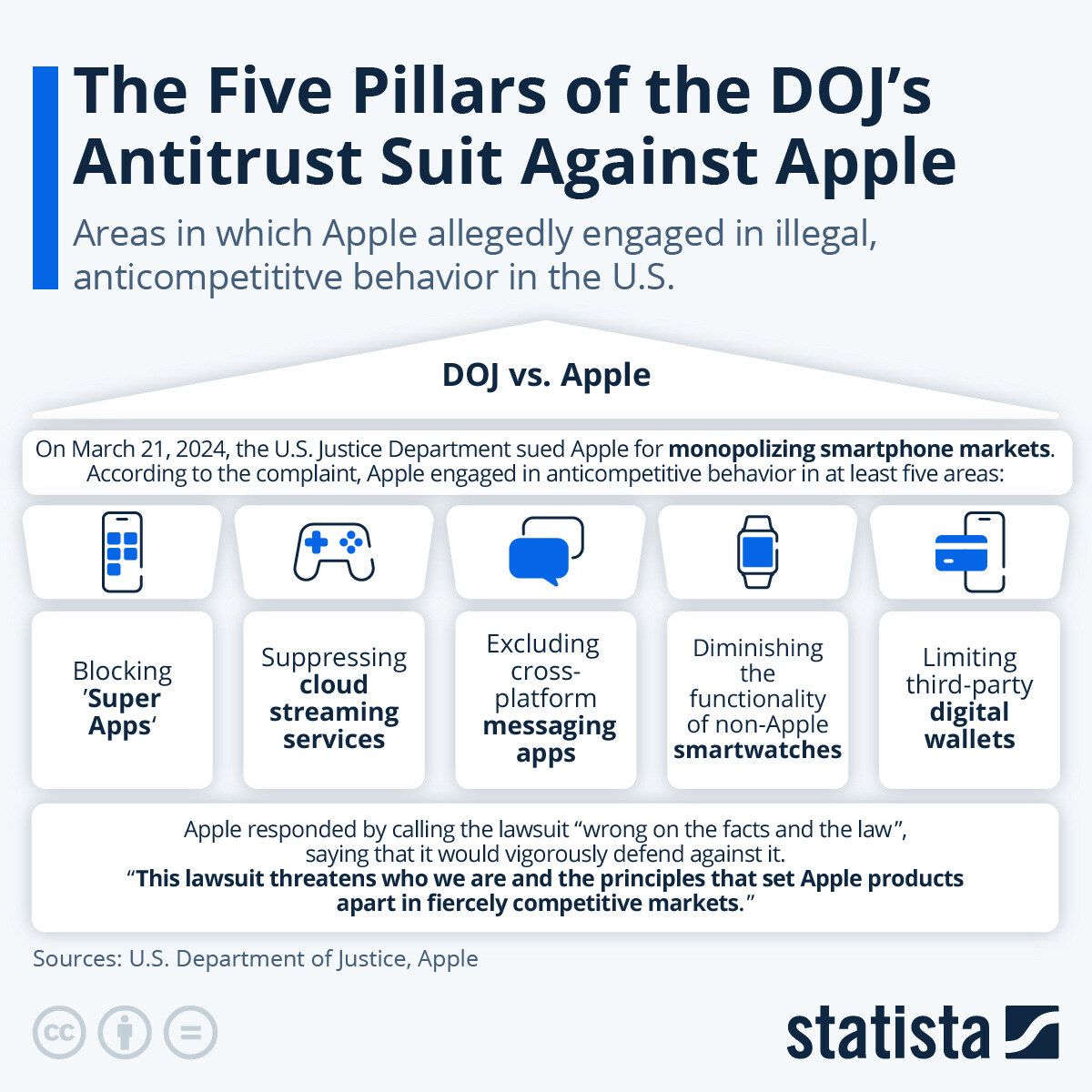
The investors have a mixed reaction to these issues, impacting Apple’s stock valuation.
Key vendors
Apple is almost entirely reliant on China with its key suppliers including Foxconn, Pegatron, and TSMC, all based in China. Although the company is now making efforts to diversify its suppliers from China, for instance, it has spent $16B for diversifying production assets away from China to India, Mexico, the US, and Vietnam (Source), China still remains an indispensable part of Apple’s global supply chains, due to its manufacturing prowess and R&D capabilities. (Source)

So naturally any event occurring in the semicon industry in China affects Apple directly. The supply chain disruptions due to geopolitical tensions between China and the US have had a heavy load on Apple’s stock.
Further, Samsung Display and LG Display are major suppliers of OLED and LCD panels for iPhones, iPads, and MacBooks. The quality and availability of displays directly influence the user experience and product appeal.
Main competitors
Companies like Samsung, Microsoft, and Google are key players whose activities can significantly impact Apple. Samsung, a major competitor in the smartphone and smart TV markets, challenges Apple with advanced technology and competitive pricing. Microsoft’s rivalry spans across operating systems, personal computing, and cloud services, directly contesting Apple’s Mac and software products. Google competes through its Android OS, which dominates global smartphone OS market share, and its hardware ventures like the Google Pixel.
Each competitor’s product launches, earnings reports, and market strategies can create fluctuations in Apple’s stock as the market reacts to shifting competitive landscapes. For instance, Samsung has overtaken Apple as the top smartphone provider in the first quarter as global shipments of iPhones fell 9.6% on year, (Source) which had hit Apple’s stock last week.
What do the consumers think?
Apple Vision Pro being the epitome of AI innovation had created quite a stir with its immersive experiences and capabilities. In fact, when Apple started taking the pre-orders in January 2024, the launch shipments sold out within hours of the launch (Source). But the buzz died very soon. Virtual Reality looks very exciting till the time its very “new” but the problem of nausea and headaches is unavoidable. Plus a heavy device is awkwardly strapped around your head which it makes it more uncomfortable.
One of the customers of Apple Vision Pro was even ready to trade his Vision Pros for Ray Ban sunglasses.
Further, the new iPhones and Macs released last year probably did not live upto the expectations of updates and new features which were expected, at the time when other companies were screaming “AI.” So now, Apple’s WWDC 2024 event is expected to release significant generative AI updates to all the devices, mainly running on-device and not relying on cloud for lower latency and data privacy. Even Siri might get much smarter with improved language models and more functionalities. The new M4 chip is also going to boost AI performance on Macs.
Nvidia
Brief Summary of the Business
Nvidia, a California-based technology company, is renowned for its graphics processing units (GPUs) that is the core pillar of modern day AI like Large Language Models. These GPUs excel at parallel processing, enabling them to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, making them ideal for complex graphics rendering. While gaming remains a significant portion of Nvidia’s business, the company has ventured into diverse areas like data centers, cloud computing, and AI.
AI Integration and Innovation
AI is deeply rooted in Nvidia’s core technology. From the time when it was started as a passion for computer graphics and 3D technology, to now where the company has contributed significantly towards developing AI. To the extent that companies in the Silicon Valley today value themselves in terms of the compute power they have owing to Nvidia’s GPUs.
These GPUs were initially made to handle complex graphics rendering for gaming and virtual environments. Over time, the parallel processing capabilities of Nvidia’s GPUs, coupled with the CUDA software platform, have proven instrumental in accelerating AI computations. This combination has fueled advancements in deep learning, where computers learn and improve independently without explicit programming.
While GPUs is a major part of Nvidia’s product line, Nvidia has built a comprehensive suite to including specialized libraries and tools to optimize and accelerate the entire range of AI applications. For instance, TensorRT - a high-performance deep learning inference platform to speed up AI applications, or the Tensor Core GPUs, its Hopper chips – the most powerful GPU chips in the market, the Blackwell architecture to support generative AI training to trillions of scale, the GeForce RTX 40 for gaming.

Nvidia’s AI software powers AI applications for enterprises, be it building generative AI models, data analytics, speech, vision or cybersecurity. Further, NVIDIA continues to invest heavily in AI research, focusing on creating more efficient, powerful, and accessible AI solutions.
Financial Performance
For the fiscal year 2024, Nvidia reported a staggering increase in its financial metrics. The company achieved a record annual revenue of $60.9 billion, which is up by 126% compared to the previous year. This exceptional growth is driven primarily by its datacenter segment, which alone brought in $47.5 billion, showing Nvidia's dominant position in AI and deep learning markets.
Quarterly performance has been equally impressive, with the fourth quarter revenue reaching $22.1 billion, marking a 265% increase year-over-year. The gross margin improved significantly to 76.0% in the fourth quarter, up from 63.3% the previous year, indicating improved profitability and operational efficiency. The net income for the fourth quarter stood at $12.3 billion, reflecting a robust increase of 769% compared to the same period last year. These figures highlight Nvidia's successful adaptation and innovation in AI technologies, which have evidently been well-received in the market (Source).
Operational Efficiencies
Nvidia’s operational performance in 2024 saw substantial achievements and significant growth across key segments. Financially, Nvidia reported record-breaking revenue figures. The company’s operational efficiency is evident in its improved gross margin, which reached 76.0% in the fourth quarter, up from 63.3% the previous year.
Despite these impressive figures, Nvidia faces ongoing challenges in its supply chain. Operational expenses also saw a 13% increase year over year, signaling rising costs associated with scaling operations and research and development.
NVIDIA holds a major market share of 92% in data centre GPUs, compared to AMD’s (Advanced Micro Devices) mere possession of 3% market share (Source). The demand for Nvidia’s H100 GPUs soared to an extent that they were being sold in black market. Nvidia is not able to cater to the rising demand. While some say that the company is purposefully holding it back to inflate the prices, the geopolitical tension may have also hampered the capability to produce since the company is heavily reliant on China’s TSMC.
While the company is facing competition from companies like not just AMD, but also its customers like Google, Meta, and Microsoft who are investing heavily to build their own compute infrastructure, Nvidia’s need to innovate continuously and maintain its technological lead places a considerable strain on its operational capacities.

Key vendors
We can broadly categorize Nvidia’s suppliers into three groups: semiconductor foundries, substrate manufacturers, and assembly & testing service providers.
Semicon Foundries: The most critical supplier for Nvidia is TSMC responsible for fabricating the majority of Nvidia’s GPUs. Any disruptions or capacity constraints at TSMC directly impact Nvidia’s ability to meet demand. Additionally, Samsung Electronics plays a smaller role in manufacturing some of Nvidia’s chips.
Substrate Manufacturers: Companies like Unimicron Technology Corp (UMC) and SEMCO provide the substrates upon which the GPU chips are mounted. Any limitations in substrate production can create bottlenecks in the supply chain, impacting Nvidia’s product availability.
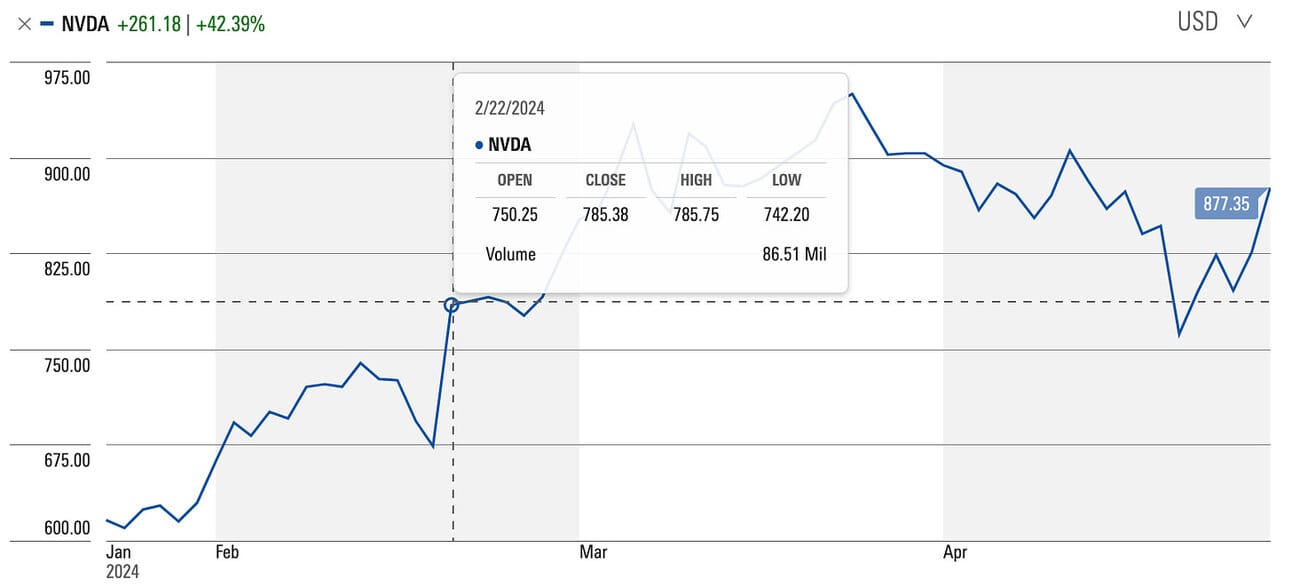
For instance, a 7.4-magnitude earthquake that hit Taiwan on April 3, 2024 disrupted operations at TSMC and UMC, which had to evacuate some of its fabrication plants and reported damage to a small number of tools, partially impacting operations (Source). Additionally, TSMC revised its growth forecasts for the semiconductor industry downwards on April 11, 2024, citing industry-wide challenges and potential decreased demand. This weighed heavily on TSMC’s stock and to some extent on Nvidia too (Source).
Assembly & Testing Service Providers: Companies such as ASE Technology Holding Co., Ltd. and Amkor Technology, Inc. handle the final stages of the manufacturing process, including assembling the GPUs into their final form and conducting rigorous testing to ensure functionality. Delays or quality control issues at this stage can also disrupt Nvidia’s supply chain.
Further, companies like Google, Microsoft, Meta, Tesla and Amazon are heavily investing in computing infrastructure, particularly in cloud services, to harness the power of AI and big data, where Nvidia is a key player. This increased investment means significant revenue generation for Nvidia (Source).
Main competitors
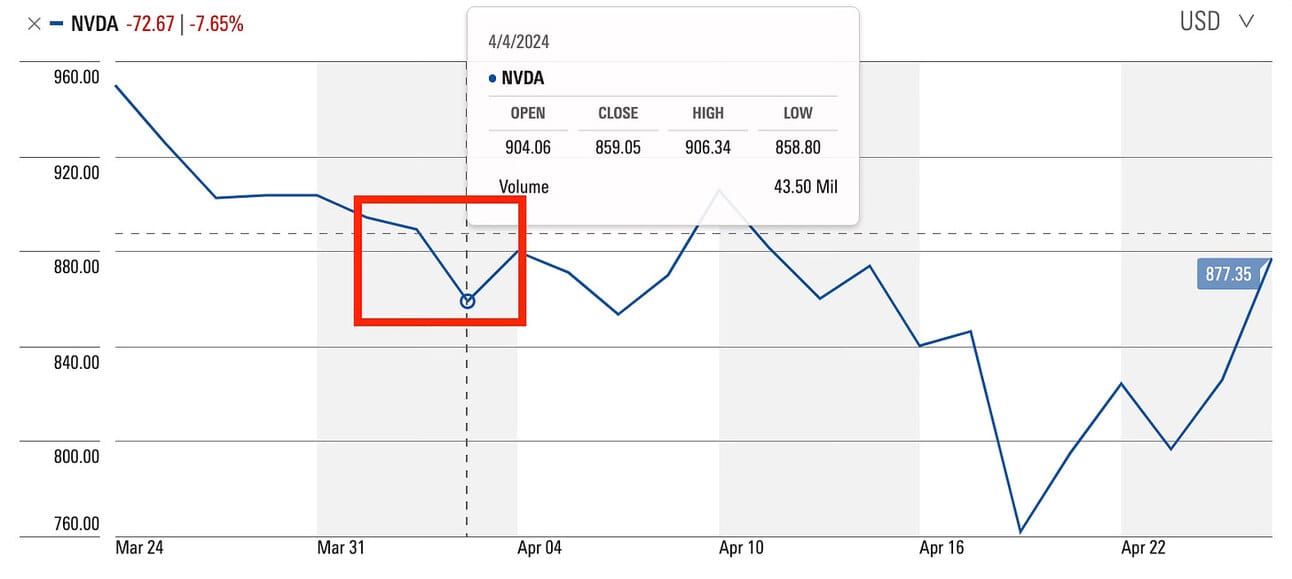
The competitive landscape for Nvidia is multifaceted, with rivals vying for market share in various segments. AMD is Nvidia’s primary competitor in the GPU market, offering a range of graphics cards for gaming, professional visualization, and data center applications. Intel, while traditionally known for CPUs, has also entered the discrete GPU market to challenge Nvidia’s dominance.
Intel’s newly launched AI chip, Gaudi 3, was a direct hit at Nvidia. Compared to Nvidia’s H100, Gaudi-3 would take half the time to train LLMs, and also delivers much faster inference.
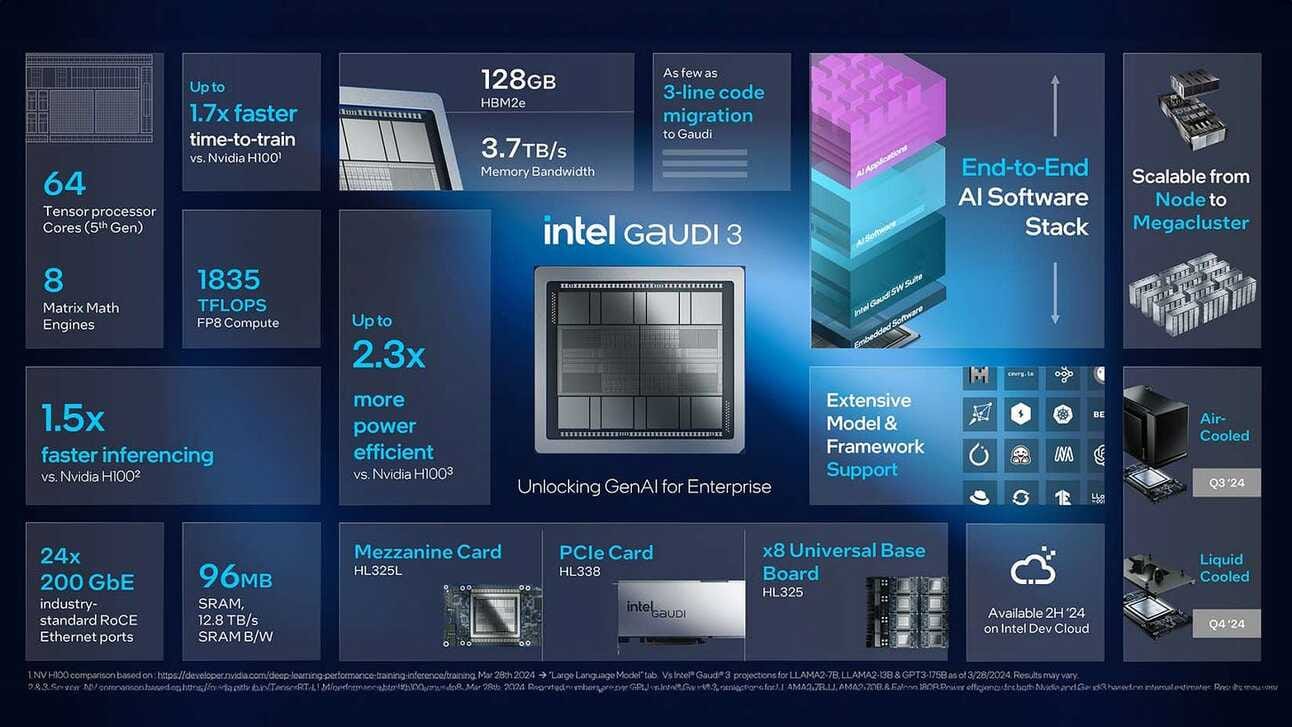
This was also one of the reasons for a dip in Nvidia’s stock on April 9.
Further, Nvidia’s own customers are now becoming its competitors. The hyperscalers like Google, Amazon, Microsoft, and Meta are increasingly developing their own AI chips to reduce reliance on Nvidia. For instance, Google has its Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), Amazon has Trainium and Inferentia chips, and Microsoft is building its Maia 100 chips. Meta too has unveiled its custom-designed AI chip, the Meta Training and Inference Accelerator (MTIA) v2👇.
While these custom solutions could hurt Nvidia’s revenue majorly, Nvidia still maintains a significant lead with its software ecosystem like CUDA, which gives it a strategic moat and mindshare among developers. Also, Blackwell architecture is set to release by next year which could boost up the demand for this high-performing hardware (Source).
In addition to the established tech giants, Nvidia also faces growing competition from emerging AI startups in the chipmaking space. Companies like Tenstorrent are developing efficient and open AI hardware that may surpass Nvidia in terms of performance per dollar and performance per watt. Sambanova focuses on creating high-performance hardware-software systems tailored for large AI workloads. Untether AI has innovated with its unique "at-memory" architecture, which enables efficient AI inference acceleration. Cerebras, another notable player, develops massive wafer-scale chips and systems specifically designed for AI workloads such as training large language models and neural networks.
These AI startups are attracting significant investment and attention, as they seek to disrupt the market with novel approaches to AI hardware. Their specialized solutions aim to address the growing demand for more efficient and cost-effective AI computation. While Nvidia currently holds a dominant position, the emergence of these innovative competitors adds further complexity to the rapidly evolving AI hardware landscape. As these startups mature and gain traction, they could potentially pose a serious challenge to Nvidia's market share and technological leadership in the coming years
What do the consumers think?
Nvidia’s GeForce RTX series graphics cards are highly regarded by gamers for their performance, features like ray tracing and DLSS, and a robust software ecosystem. Gamers generally appreciate the consistent performance improvements and innovative technologies offered by Nvidia.
Professionals in fields such as video editing, 3D animation, and graphic design rely on Nvidia’s Quadro and RTX GPUs for their powerful capabilities and specialized software optimizations.
Nvidia’s data center GPUs, such as the A100 and H100, are widely used in AI research and training, as well as high-performance computing applications. The consumer sentiment is evident with the high demand for Nvidia’s solutions.
However, the high cost of Nvidia’s high-end GPUs is a barrier for some consumers, particularly budget-conscious gamers. Further, supply chain constraints and high demand have led to limited availability of the GPUs, which has driven the industry in general to look for alternate options.
Alphabet (Google)
Brief Summary of the Business
Alphabet stands as a behemoth in the tech industry, known primarily for its Google search engine which dominates the global market. Google also offers a broad spectrum of products and services including Android OS, Google Cloud, advertising services, YouTube, and hardware products like Google Pixel phones and Google Home smart speakers. The company’s business model is heavily reliant on advertising revenue, though it has been diversifying into cloud computing and consumer hardware to expand its revenue streams.
AI Integration and Innovation
AI today is the backbone of all the products and services Google offers, be it ranking and recommendation in search and streaming, running Android, powering Google Assistant in its phones, maps, image recognition in Photos, or numerous tools available on the Google Cloud.
Immersive View in Google Maps (Source: Google)
Google’s AI journey began in the mid-2000s when AI was first used to refine Google Search algorithms, leading to more relevant search results. This foundational step evolved into more complex applications like Google Translate and voice recognition in Android devices.
The acquisition of DeepMind in 2014 escalated the pace of research and integration of AI in Google. Google introduced Google Assistant in 2016, its AI-driven virtual assistant, and also integrated AI into Google Photos for automatic tagging and facial recognition. Since then, generative AI and NLP has been a prime focus, as was also seen industry-wide.
Google’s foray into generative AI now includes its AI chatbot powered by the very powerful Gemini models, opensource Gemma models, Imagen for generating images, Gemini integrated across all the productivity applications like Docs, Sheets, Mail, and even a separate platform Vertex AI for building and testing AI models.
Financial Performance
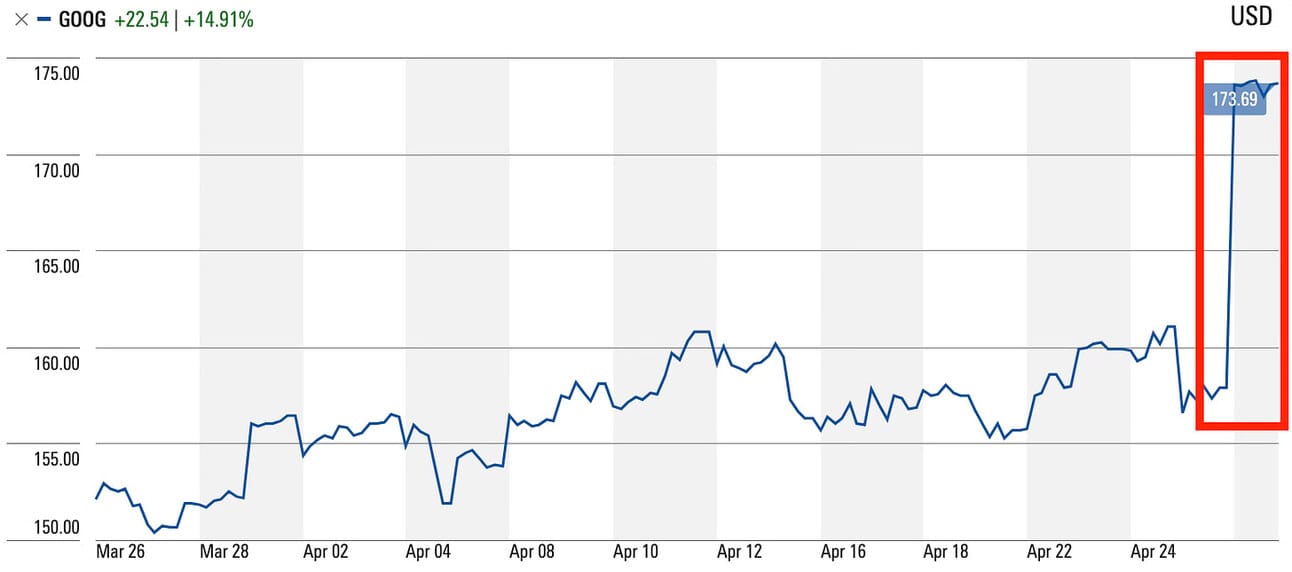
Alphabet Inc. reported stellar financial results for the first quarter of 2024, surpassing analysts’ expectations across key metrics. The tech giant’s revenue soared to $80.5 billion, marking an impressive 15% year-over-year increase and outperforming the consensus estimate of $78.7 billion. The company’s net income skyrocketed by 52% to $20.7 billion, translating to earnings per share of $1.89, significantly higher than anticipated.
The robust performance was driven by strong demand for online advertising, with Google Search and Other advertising revenue reaching $46.2 billion, ahead of the $45 billion consensus. YouTube advertising also exceeded expectations, generating $8.1 billion in revenue compared to the projected $7.7 billion. (Source)
Additionally, Google Cloud continued its momentum, reporting a 28% year-over-year growth to $9.6 billion, surpassing the $9.4 billion forecast. The cloud unit’s profitability further solidified, with an operating income of $864 million in Q4 2023, a remarkable turnaround from the $186 million loss in the year-ago quarter. (Source: Barron, CNBC)
These strong results also led to a huge uptick in Alphabet’s stock.
Operational Efficiency
Alphabet has been on a cost-cutting spree since last year in anticipation of slower ad growth and increased spending on AI, including workforce reductions and optimizing office space. These measures led to substantial one-time charges due to employee severance and office space exits. Despite this, Alphabet maintained a strong operating income of $23.7 billion for the quarter.
The company is heavily investing in AI, particularly with its Gemini models, and seeing positive results in terms of user experience, efficiency, and potential for monetization across various products. The company has achieved significant improvements in machine learning efficiency, reducing costs and improving performance.
However, as the AI landscape evolves rapidly with intensifying competition. Alphabet must maintain its innovation pace and effectively monetize its AI investments to sustain its growth trajectory. Additionally, transitioning existing products to incorporate AI functionalities requires a delicate balance between user experience, cost efficiency, and effective monetization strategies. (Source)
Main competitors
Google’s main competitors, including Microsoft, Meta, Amazon, Anthropic and OpenAI have posed challenges to Google’s dominance in various sectors, leading to concerns about the company’s future growth prospects but also pushing innovation by the company.
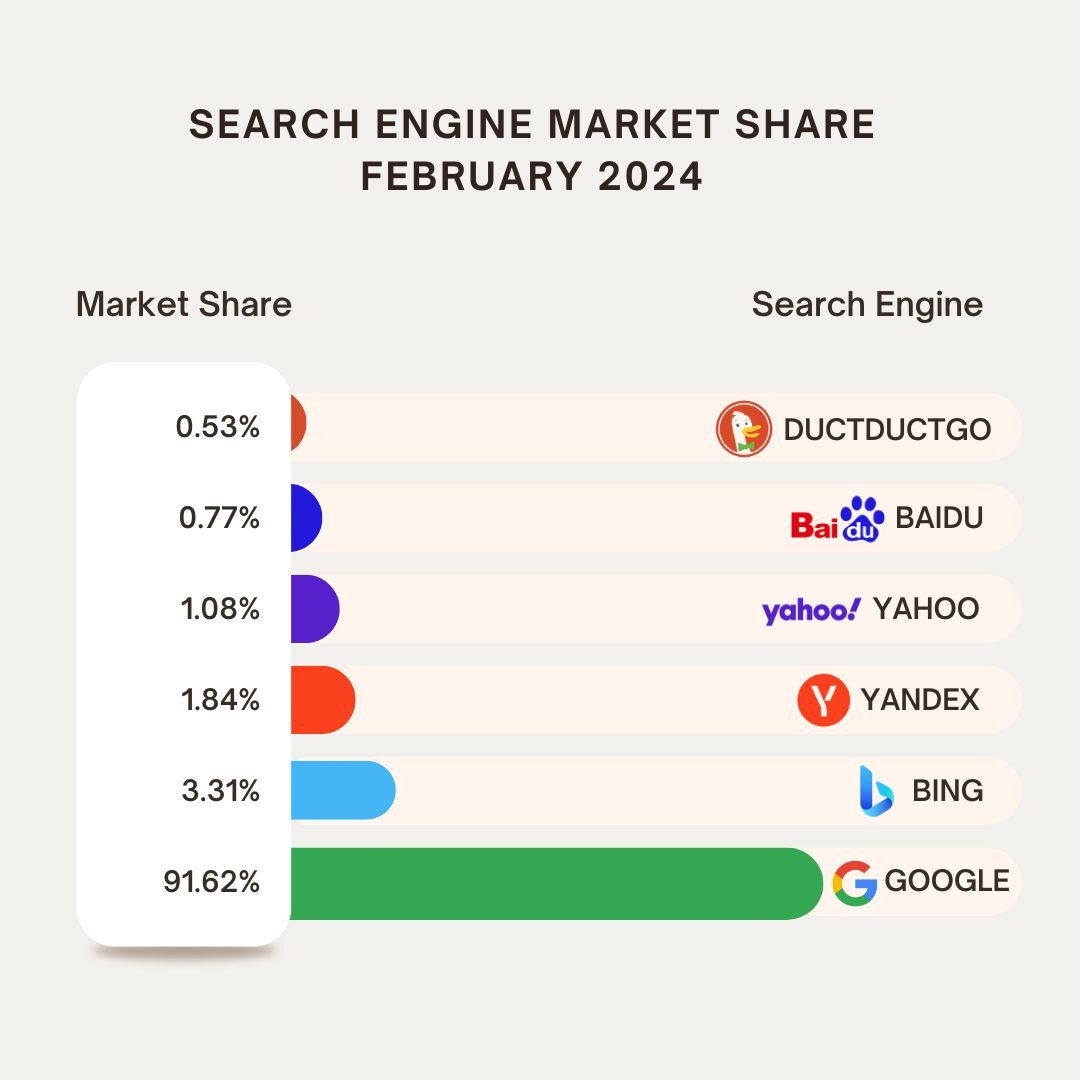
Microsoft’s cloud and AI services, particularly Azure and its integration with OpenAI’s ChatGPT, have posed a challenge to Google’s dominance in search and cloud computing. In February 2024, a report that OpenAI was developing a web search product to compete with Google caused Alphabet’s stock to fall by as much as 3.8% (Source). However, Google continues to dominate with a staggering 91% share.
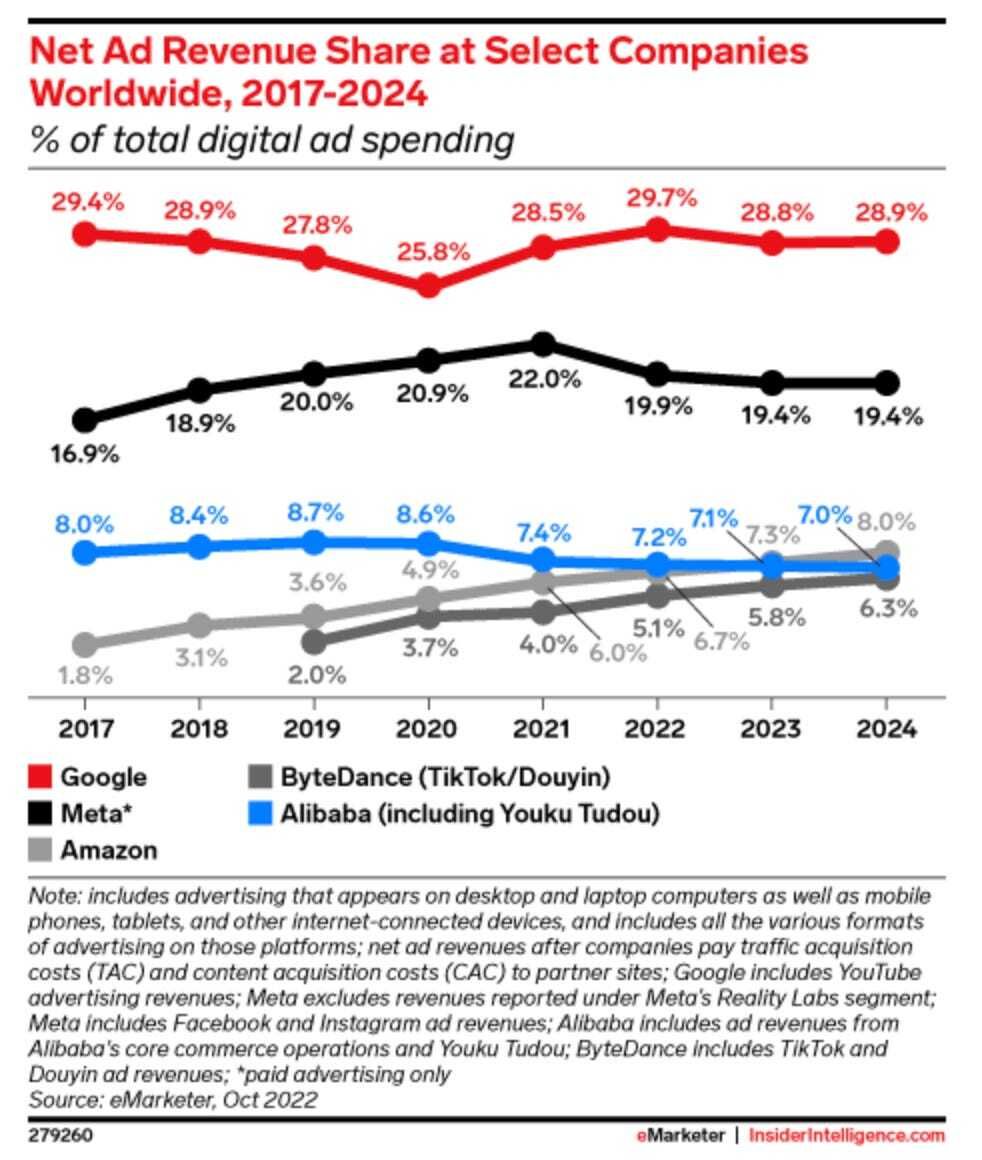
Meta’s advertising growth has outpaced Google’s in recent quarters, suggesting a potential shift in the online ad market dynamics. This has raised concerns about Google’s share of search and total advertising dollars. Similar to Meta, Amazon’s advertising growth has also outpaced Google’s, contributing to the concerns about Google’s dominance in the online ad market (Source).
What do the consumers think?
Google’s AI products and services are being widely used by individuals, developers and business, be it for productivity, coding, research, or media generation. When OpenAI had released ChatGPT and further iterations, it seemed Google came under pressure to hurriedly roll out products which weren’t probably ready yet. And the company faced the consequences! Its previous AI chatbot Bard had a reputation of hallucinating the most. Just a couple of months back, Google landed in a big controversy as its text-to-image AI generator was being called “woke and anti-racist” refusing to generate pictures of white people.

However, Google released the Gemini Pro models which turned around the image. Its performance is similar to OpenAI’s GPT-4 and Anthropic’s Claude-3 models, with the added benefit of a humongous context and the ability to process audio and video inputs as well.
AI integrated with other products like Search, Photos, and Maps has also received a positive feedback. The AI-generated answers in Search have helped to cut the noise and get the relevant information quickly with citations, but can also limit information discovery and make it ChatGPT-like (9to5Google). Google has been further innovating Search to make it more easy and intuitive with Circle and Scribble to search for information.
AI in Google photos is now a staple for many to find photos based on face recognition and object detection, while the animations enhance the overall experience. AI in Google Maps has also helped in discovering new places with simple queries and enhanced the experience with immersive views.
While Gemini in Google Workspace has helped in generating content, drafting emails, and analysis in Sheets, it has received mixed reviews as it stumbles in sensitive topics. (Techcrunch). Vertex AI, a platform for building and scaling AI models, is also acclaimed for its user-friendliness, simplifying machine learning workflows, and is particularly useful for those with limited coding experience, giving tough competition to Amazon SageMaker. (Trustradius)
Microsoft
Brief Summary of the Business
Microsoft is a global technology leader that develops, licenses, and supports a wide range of software products, services, and devices. Its core products include the Windows operating system, Microsoft Office suite, and cloud services through Microsoft Azure. As a pivotal player in the digital transformation of industries, Microsoft also focuses on AI development, enterprise solutions, and personal computing devices.
AI Integration and Innovation
Microsoft has been at the forefront of integrating AI into its core products and services. The company has made huge investments in AI research and development, majorly in generative AI. Its most strategic investment has been in OpenAI, the creator of ChatGPT, to the tune of $13 billion (source). The partnership has provided Microsoft with access to OpenAI’s leading research and expertise in AI, integrating the latest GPT-4 model across products like the Microsoft Office, Copilot in Bing, and Microsoft Azure, and Codex model in GitHub Copilot.
This integration has strengthened Microsoft’s position in the market, giving a tough competition to companies like Google in services like productivity apps, cloud computing and search business (however, Google is still the most dominant player) (Source).
Besides OpenAI, Microsoft has made many strategic partnerships with companies like Nvidia focusing on optimizing Azure for AI workloads by leveraging Nvidia's GPUs and AI software. This collaboration is to enhance the performance and efficiency of AI applications running on Azure, catering to the growing demand for AI-powered solutions. The partnership also extends to NVIDIA AI Enterprise software suite, providing enterprises with advanced AI tools and frameworks within the Azure environment. (source)
Financial Performance
Microsoft reported strong financial results for the third quarter of fiscal year 2024, underlining the sustained growth trajectory of its diversified product and service portfolio. The company achieved a revenue of $61.86 billion, marking a 17% increase year-over-year. This growth was significantly buoyed by its cloud services, particularly Azure, which alone saw a 31% increase. This reflects Microsoft’s ongoing strategic focus on cloud computing, a core area of interest for AI professionals given the cloud’s critical role in scaling AI solutions (Microsoft) (MarketBeat).
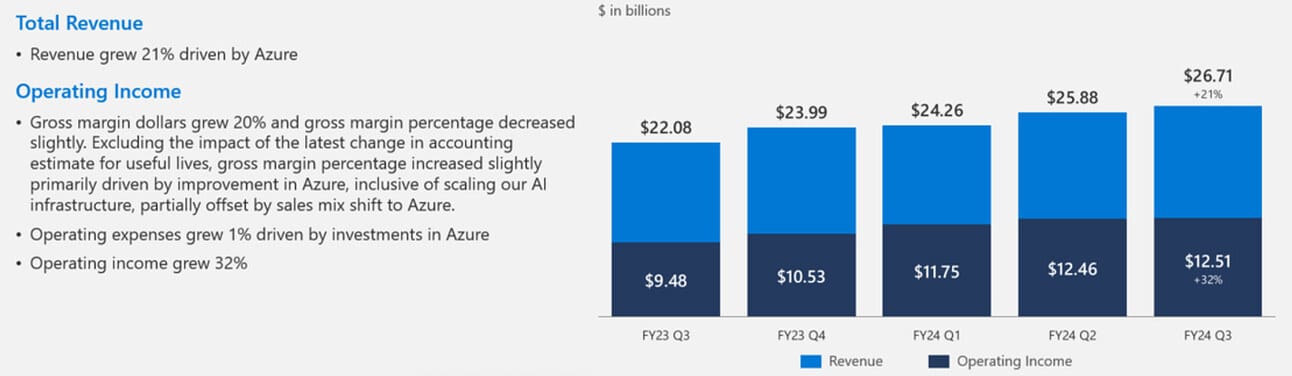
Operating income for the quarter stood at $27.58 billion, up by 23% compared to the same period last year. Net income rose to $21.94 billion, with earnings per share increasing to $2.94, exceeding analyst expectations by $0.13. Such financial outcomes not only reflect Microsoft’s effective market strategies and operational efficiency but also the increasing potential of innovation and adoption of technology, particularly AI.
Operational Efficiencies
Microsoft aggressively pushed into the AI space, impacting both their product offerings and internal operations. Azure, the cornerstone of their cloud business, saw significant growth fueled by AI services and large-scale migrations. Interestingly, the growth wasn’t solely attributed to standalone AI projects; rather, a synergy emerged where AI adoption spurred demand for adjacent Azure services like vector databases (Azure Search), data platforms (Fabric, Cosmos DB), and developer tools. This indicates a shift towards holistic AI-powered solutions rather than isolated implementations.
The emphasis on Copilot Studio, which allows businesses to customize copilots with their own data and integrate with existing SaaS applications, further suggests a move towards tailoring AI solutions to specific business needs and workflows. This approach is likely to drive deeper integration of AI within organizations, moving beyond mere experimentation to tangible process optimization and efficiency gains.
However, Microsoft acknowledged that current AI demand outpaces their infrastructure capacity, necessitating substantial capital expenditure to bridge the gap. This constraint may impact the pace of AI service expansion and user onboarding in the near term. Additionally, while Microsoft currently leads in the enterprise AI space, competition is intensifying as other companies develop their own copilot solutions.
Key vendors
Microsoft’s reliance on key semiconductor manufacturers like AMD and Nvidia is crucial for powering its Azure services with the latest AI accelerators. These partnerships are vital for Microsoft’s ability to offer cutting-edge cloud solutions, particularly in AI and machine learning. The integration of advanced GPU technologies from Nvidia and high-performance CPUs from AMD ensures that Azure remains competitive in the cloud computing market.
Disruptions in the supply chain or significant advancements from these suppliers directly affects Azure’s operational capabilities and efficiency, impacting Microsoft's stock performance. For instance, a recent collaboration between Microsoft and Nvidia integrates Nvidia’s advanced GPU technologies with Microsoft Azure to enhance Azure’s AI computing capabilities was visible on Microsoft’s stock. (Source)
Also, Microsoft’s strategic partnership with OpenAI significantly influences its AI offerings, including Azure OpenAI Service and various Copilot applications as OpenAI’s advancements in AI models ensure that Microsoft remains at the forefront of AI technology.
Main competitors
Microsoft’s main competitors include Apple, Google, Oracle, IBM, and Salesforce. These companies compete with Microsoft across various business segments such as operating systems, productivity software, cloud computing, and enterprise software.
Apple is a major competitor to Microsoft, especially in the personal computing and mobile device markets. Recently, Microsoft briefly overtook Apple as the world’s most valuable company by market capitalization, driven by stronger growth expectations for Microsoft’s cloud and AI businesses compared to challenges faced by Apple in the smartphone market. (source)
Google competes with Microsoft in search, cloud computing, productivity software, and AI models like LLMs and creative generative AI models. In the cloud computing space particularly, AWS is the market leader, closely followed by Microsoft Azure. Google Cloud, while smaller, is also a strong competitor in this space.
Salesforce is a key competitor in the customer relationship management (CRM) software space, where it competes with Microsoft’s Dynamics 365 offerings. The competitive landscape in this market impacts Microsoft’s growth and market share in the enterprise software segment.
What do the consumers think?
Microsoft’s AI-powered products, particularly the Copilot series across applications like Word, Excel, and GitHub, have garnered mixed reactions from users. While many appreciate the productivity enhancements—such as automated document summarization, data analysis, and integration within the Microsoft ecosystem—there are notable concerns. These include the sometimes slow response times of Copilot and its limitations with complex data tasks, which could deter more technical users. Furthermore, Copilot’s dependency on an internet connection and storage in OneDrive may not appeal to all users. (Source)
Business users have given Microsoft’s AI assistant, Copilot for Microsoft 365, a range of reviews, highlighting its utility in streamlining tasks like meeting summarizations and document creation. However, some focus on its price of and occasional inaccuracies in more complex tasks like data manipulation in Excel and generating meeting summaries. (Source)
The overall impact and acceptance of Microsoft’s AI, including products like Bing’s AI-powered search and GitHub Copilot, vary, with some products like Bing not meeting market expectations. Despite these mixed reviews, Microsoft reports significant uptake of its AI offerings, suggesting a strong market interest driven by their potential to transform workplace productivity.
Tesla
Brief Summary of the Business
Tesla, led by the enigmatic Elon Musk, has transitioned from a niche electric vehicle manufacturer into a diversified technology powerhouse. Beyond its core electric vehicle (EV) offerings, Tesla is actively involved in battery energy storage solutions (Powerwall, Megapack), solar energy systems (Solar Roof), and self-driving technology development (Full Self-Driving). The company's ambitious vision extends to robotaxis, humanoid robots, and even interplanetary travel through SpaceX.
AI Integration and Innovation
AI is deeply woven into Tesla’s operations and future ambitions. The company’s Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD) technologies are perhaps the most prominent examples. These systems utilize a complex neural network architecture, processing data from cameras, radar, and ultrasonic sensors to enable features like adaptive cruise control, lane keeping, automatic lane changing, and autonomous navigation. Tesla’s approach involves training its AI models on a vast dataset of real-world driving data collected from its fleet of vehicles, continuously refining and improving their capabilities through over-the-air updates.
Beyond autonomous driving, AI plays a crucial role in optimizing Tesla’s manufacturing processes, managing energy storage and distribution, and even designing new vehicles. The company’s Dojo supercomputer, specifically designed for AI training, is evident how deeply AI is integrated into all the dynamics of Tesla.
One of Tesla’s most intriguing AI ventures is the development of its humanoid robot, Optimus. Optimus is intended to perform a range of tasks, from mundane chores to complex industrial operations, utilizing the same AI technology that powers Tesla’s self-driving cars. This includes computer vision for navigating its environment, and decision-making algorithms for interacting with objects and performing tasks. Optimus is still in its development stages.
Financial Performance
In the first quarter of 2024, Tesla faced a challenging period with its financial results failing to meet the Street expectations. The company reported earnings of $0.45 per share on revenues of $21.3 billion, missing the projected figures of $0.49 per share on $22.2 billion in revenue. This shortfall occurred despite Tesla’s substantial investment in AI training compute, which saw an increase of over 130% during the quarter. The financial miss was attributed to several factors, including a significant $2.7 billion increase in inventory and a $1 billion expenditure on AI infrastructure. However, Tesla’s cash reserves remained robust, albeit reduced, totaling $26.9 billion at the end of the quarter.
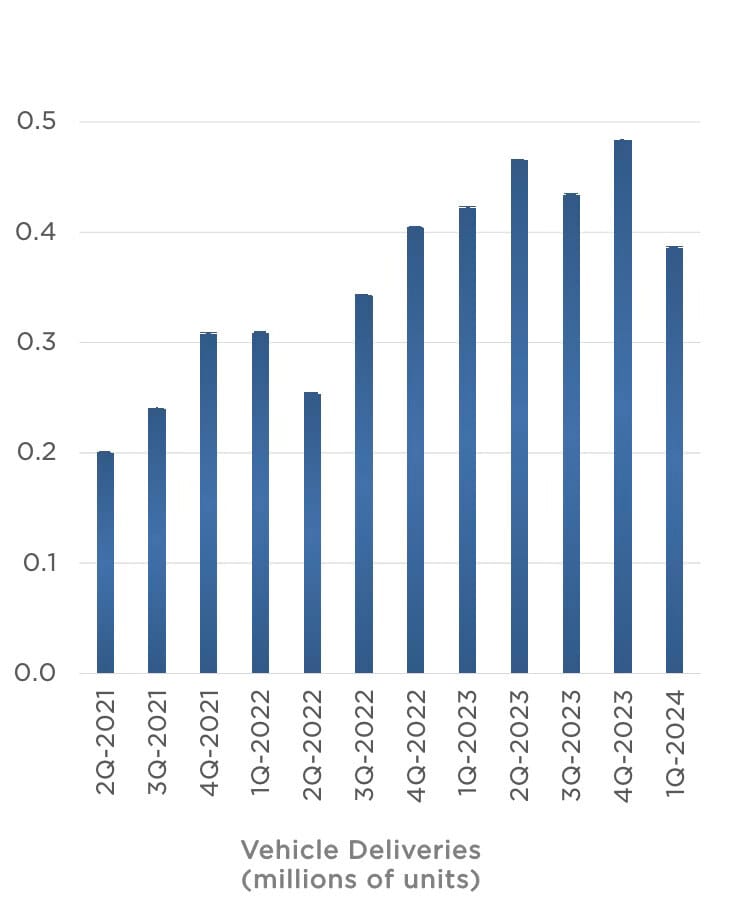
Production and delivery figures also highlighted challenges, with Tesla manufacturing 433,000 vehicles but only delivering 387,000, marking a 9% decrease year-over-year. This was significantly below the company's previous performance in the last quarter of the previous year, which saw record deliveries. The dip was partly due to logistical issues and operational disruptions, including the effects of regional conflicts and an arson attack at one of its factories. Despite these setbacks, Tesla maintained its position as the leader in global battery electric vehicle sales, overtaking competitors like China’s BYD once again in the EV market (TeslaNorth.com) (Electrek).
Operational Efficiencies
Tesla’s Q1 2024 operational performance was a mixed bag, showcasing both challenges and successes. The company faced headwinds from various factors, including a complex Model 3 Highland retooling process, potential supply chain disruptions, and a broader economic slowdown impacting EV adoption. Additionally, disruptions at the Berlin factory and inventory mismatches further strained profitability and free cash flow. However, Tesla demonstrated resilience through strategic cost-cutting measures, such as a 10% headcount reduction projected to save over $1 billion annually.
Despite the challenges, Tesla achieved notable operational improvements. The company successfully reduced per-unit costs, contributing to maintaining profitability despite price adjustments. Production efficiency at the Austin and Berlin Gigafactories for the Model Y is approaching the levels seen at the Fremont factory, indicating progress in optimizing manufacturing processes.
Looking ahead, Tesla maintains an optimistic outlook. The company anticipates significant growth in energy storage deployments throughout 2024, with projections indicating a 75% increase compared to 2023.
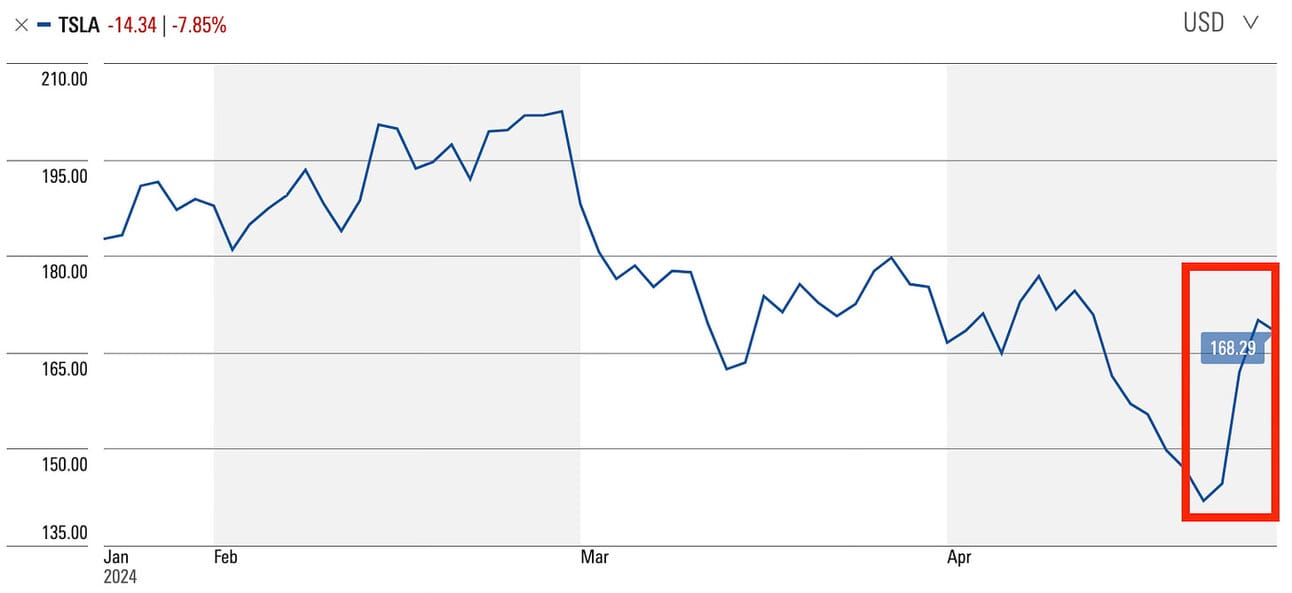
Additionally, Tesla’s plans to accelerate the launch of more affordable electric vehicle models, which will incorporate elements from its suppliers, caused its stock price to jump around 10% on April 24, 2024 as investors got confidence in the company’s growth.
The company remains committed to its ambitious goals, including large-scale deployment of Full Self-Driving technology and further advancements in AI, utilizing the savings from operational efficiency improvements and idle compute capacity to fuel future innovation. (Source)
Key vendors
Tesla’s production is significantly influenced by its strategic relationships with a network of key suppliers who provide essential materials and components for its electric vehicles and battery production. Among these, companies like Panasonic, LG Chem, CATL, and Samsung are pivotal. Panasonic and LG Chem supply the crucial battery cells that power Tesla’s vehicles, while Samsung provides advanced microchips critical for Tesla's self-driving technology. CATL, another major player, supplies nickel-free LFP batteries, essential for maintaining production cost-efficiency amid fluctuating raw material prices (Value Investors Central) (The Driven).
The impact of these suppliers on Tesla’s operations extends into strategic commodity sourcing, with companies like Vale ensuring a steady supply of nickel essential for battery production. This relationship is particularly crucial as it secures the raw materials needed amidst a global rush for battery components, which is critical given the sharp rise in demand for electric vehicles and the corresponding need for high-volume, high-quality battery production (Electrek).
However, Tesla’s reliance on these suppliers also introduces vulnerabilities. Production setbacks due to global supply chain disruptions, including those caused by geopolitical tensions and specific incidents like the arson attack at Tesla’s Berlin Gigafactory, have directly impacted delivery numbers and financial performance. (Electrek) (UPI).
Main competitors
BYD, a Chinese automaker, has emerged as a major competitor to Tesla. In the last quarter of 2023, BYD surpassed Tesla in global sales of pure-play electric cars. BYD’s competitive pricing, with vehicles costing a fraction of Tesla’s prices, has helped propel its rise. This has put significant pressure on Tesla’s stock price, which is down over 40% so far in 2024.
Other Chinese EV manufacturers like Nio, Xpeng, and Li Auto have also been aggressively competing with Tesla in the Chinese market, the world’s largest auto market. These companies have been slashing prices to gain market share, leading to a price war. For example, in April 2024, Li Auto announced price cuts of up to 30,000 yuan ($32,000) for its models, while Tesla reduced the starting price of its Model 3 in China by 14,000 yuan.
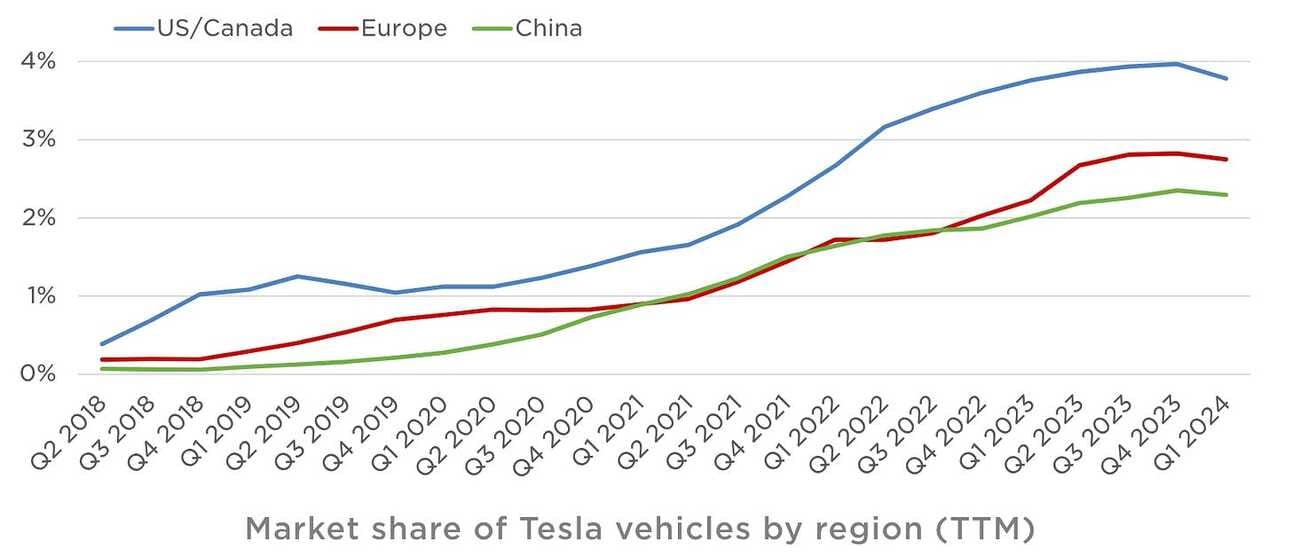
Further, legacy automakers have also been investing heavily in EVs. Tesla’s market share in the US EV market has been steadily declining. In Q1 2024, Tesla’s market share fell to 51.3%, down from 61.7% a year earlier. This represents the lowest market share for Tesla on record, dropping from nearly 65% for the full year 2022. The key reasons behind this decline include the increasing competition from new EV startups as well as established automakers like Hyundai, BMW, Mercedes, and Ford, all of which have gained market share by releasing their own EV models.
To counter the competition, Tesla has announced plans to produce more affordable EV models as early as late 2024 or early 2025, with prices as low as $25,000. However, the success of these models remains to be seen. (MotleyFool, CNBC, CNN)
What do the consumers think?
Tesla’s electric vehicles are celebrated for their technological sophistication, high performance, and energy efficiency, which mark them as top contenders in the electric car market. Owners appreciate the advanced features like the mobile app, sentry mode, and over-the-air software updates, which enhance the user experience by making the cars smarter and more connected. The safety features and driving performance of Tesla cars also receive high praise, positioning them favorably among consumers looking for sustainable and innovative transportation solutions. (Teslarati)
However, despite the advanced technology and positive user experience, Tesla faces criticism regarding the build quality of its vehicles, particularly the higher-end models like Cybertruck which some users feel do not match the standard set by traditional luxury automakers.
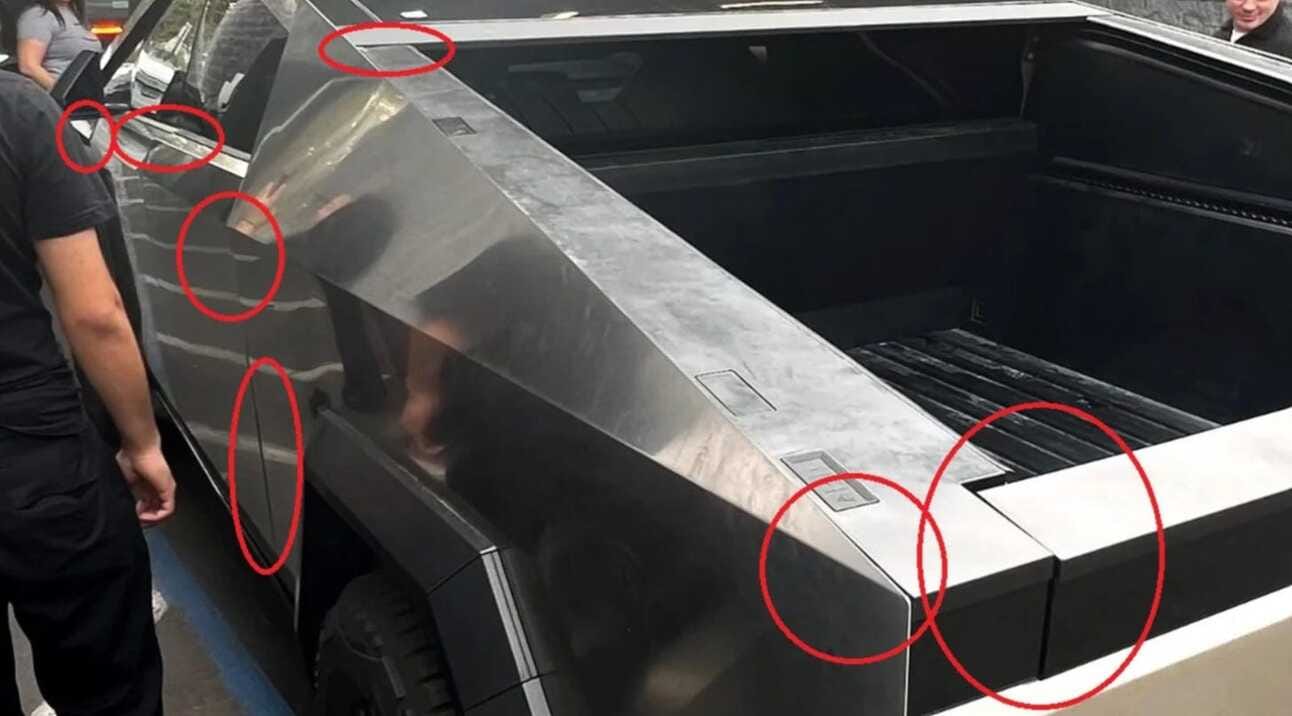

Concerns also extend to Tesla’s FSD technology. Despite being marketed with ambitious claims, Tesla’s FSD remains a Level 2 automation system requiring significant driver engagement, contrary to the implications of its name. The company has been aggressively enticing customers to upgrade to the latest FSD version by significantly slashing the price to $99 a month, to collect more data and train its technology for being fully autonomous.
Meta
Brief Summary of the Business
Meta, originally Facebook, has grown from a single social networking platform to a vast conglomerate specializing in digital communication and connectivity. The company now operates through two main segments: the Family of Apps and Reality Labs. The Family of Apps includes Facebook, Instagram, Messenger, and WhatsApp, which collectively serve to connect billions of people. Reality Labs focuses on developing augmented and virtual reality products, pushing the boundaries of how users interact with digital content in more immersive ways.
AI Integration and Innovation
Meta has significantly advanced in integrating AI across its platforms and operations. The company has heavily invested in developing advanced AI models and techniques to enhance user experiences, improve content moderation, and drive business growth.
One key area of AI innovation at Meta is NLP. The company’s latest release Llama 3 models are the best opensource models available today, competing with very advanced models like GPT-4 and Claude-3 models from Anthropic. Meta’s new in-house Meta AI chatbot powers more natural and engaging conversations on its websites and apps. This allows users to interact with AI-powered assistants in a more human-like manner.
Meta Reality is also pushing towards developing the metaverse, an interconnected digital reality leveraging VR and AR technologies. AI plays a crucial role in this vision, powering virtual environments where people can interact more naturally and fluidly.
Additionally, Meta is leveraging computer vision AI to enhance features like automatic image captioning, object detection, and augmented reality filters on Instagram and Facebook. These AI-powered capabilities enable users to better navigate and engage with visual content on the platforms.
Meta has deployed AI systems to detect and remove harmful or violative content at scale. By training machine learning models on vast datasets, the company can more efficiently identify and take action against misinformation, hate speech, and other problematic material. This helps maintain the integrity and safety of its platforms.
Financial Performance
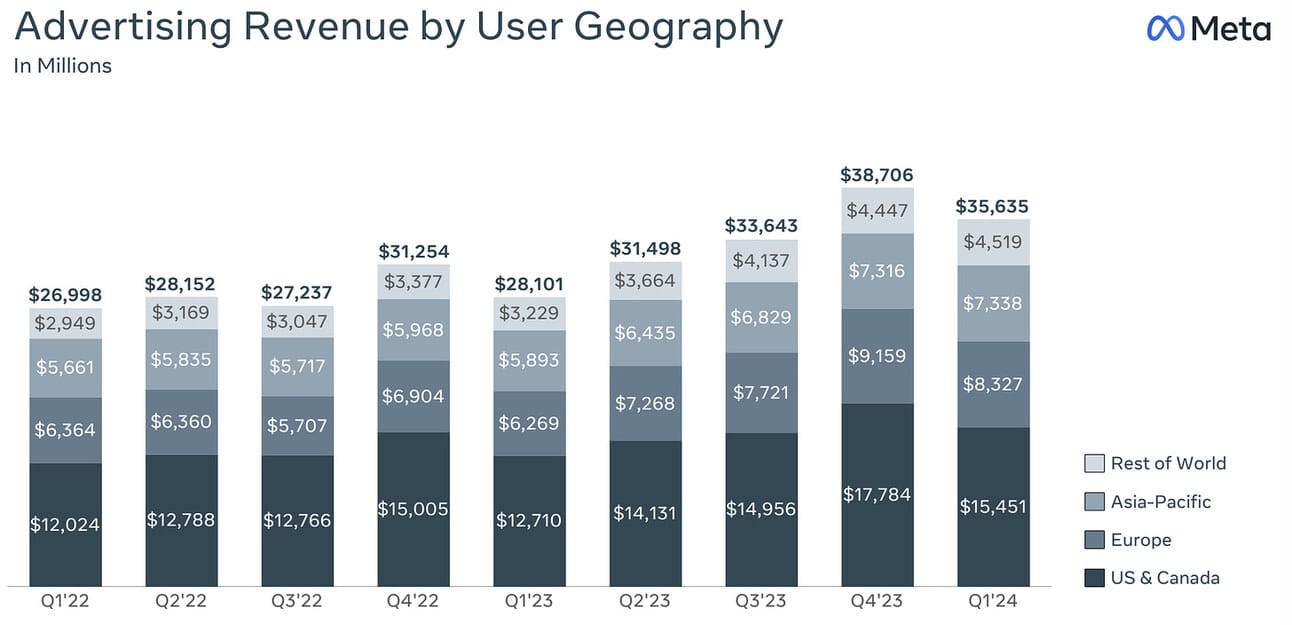
Meta Platforms reported a strong financial performance in Q1 2024, achieving significant growth across key financial metrics. The company reported revenue of $36.46 billion for the quarter, marking a 26% year-on-year increase from $28.6 billion in the previous year. This growth was the highest quarterly increase since Q3 2021. EPS also saw a substantial rise, reaching $4.71, which exceeded analyst expectations by $0.39 and nearly doubled from $2.20 the year before.
The company’s profitability also improved, with a net profit margin of approximately 31.1%. This represents a significant improvement from 19.9% in the same quarter of the previous year, although slightly lower than the 35.0% margin in Q4 2023. Meta’s ad revenue, which constitutes more than 96% of its total revenue, benefitted from strong demand across various verticals, particularly online commerce and gaming, suggesting a healthy outlook for sustained growth (Meta, IG.com)
Operational Efficiencies
Meta’s Q1 2024 results paint a picture of a company undergoing a strategic shift. While its family of apps, boasting 3.2 billion daily users, continues to thrive with a 27% year-over-year revenue increase, Meta is placing significant bets on its future: AI and the Metaverse. The launch of Meta AI, powered by the Llama 3 model, is a key development, with tens of millions of users already engaging with the platform. Furthermore, AI-driven content recommendations now influence 30% of Facebook feed content and over 50% on Instagram, driving user engagement and creating fertile ground for future monetization.
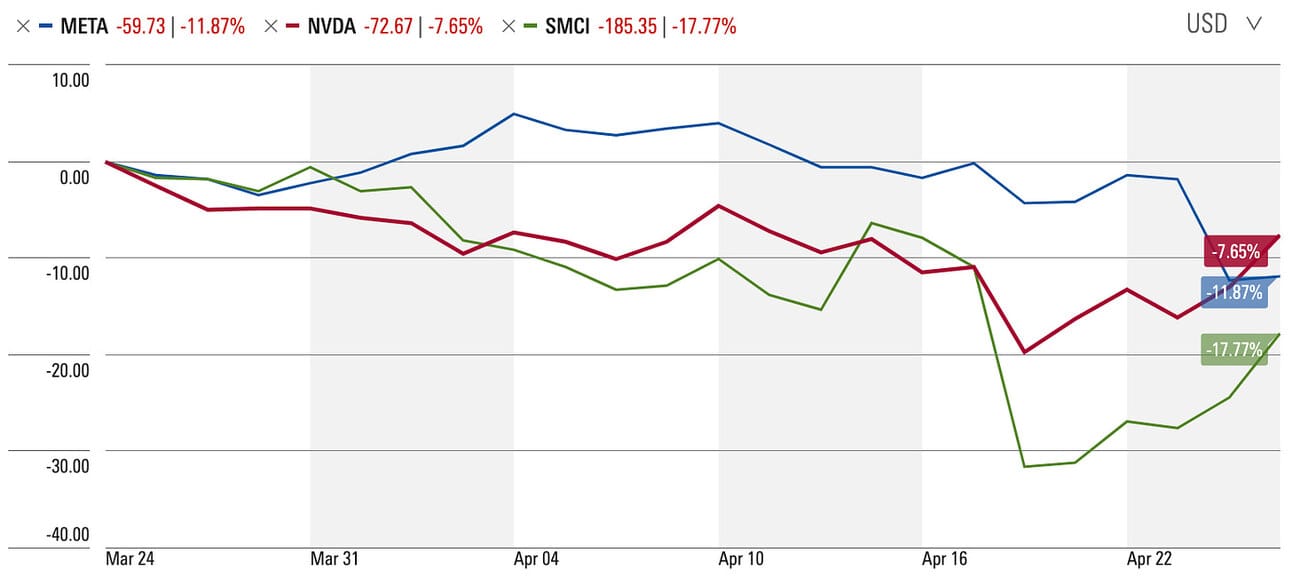
Despite these advancements, Meta acknowledges that its ambitious AI and metaverse pursuits necessitate a multi-year investment cycle. This translates to a projected CapEx range of $35-40 billion for 2024, a significant increase driven by AI infrastructure needs. This announcement alone rose stock prices of companies like Nvidia and SMCI and cost heavy to Meta’s investors (Source).
Additionally, Reality Labs, the division spearheading metaverse development, is expected to see operating losses deepen as it expands its product offerings and ecosystem. This focus on long-term innovation may impact short-term profitability, demanding careful balancing of resource allocation and operational efficiency.
However, Meta remains confident in the transformative potential of AI and the metaverse. Early successes, such as the doubling of revenue from AI-powered ad tools, demonstrate the value these technologies can unlock.
Key vendors
Meta’s aggressive push into AI is heavily reliant on strategic partnerships with key technology providers. One prominent collaboration is with NVIDIA, supplying high-performance GPUs for Meta’s AI research superclusters. These clusters, equipped with thousands of NVIDIA A100 and H100 GPUs, provide the computational power needed to train and deploy massive AI models like Llama 3 and drive advancements in generative AI, computer vision, and natural language processing.
Beyond hardware, Meta strategically partners with companies like Essilor Luxottica to expand its reach into the wearable tech market. The Ray-Ban Meta smart glasses, born from this collaboration, serve as a platform for Meta’s AI assistant, showcasing the convergence of AI and metaverse initiatives.
(Source: Meta)
Meta’s open ecosystem approach extends to its Meta Horizon OS, which will expand its partnerships with hardware manufacturers, software developers, and content creators. This will grow the mixed reality ecosystem by fostering diverse applications and experiences beyond Meta’s first-party offerings.
Main competitors
Often seen as a collaborator as well as a competitor, Nvidia supplies crucial GPU hardware that powers AI operations, including those at Meta. However, Nvidia’s own advances in AI technologies also position it as a direct competitor in areas like AI model training and neural network applications.
Google is a major competitor in AI through its extensive range of AI-driven products and services, including Google Assistant, AI-enhanced search functionalities, AI models including the Gemini, and various enterprise AI solutions, put pressure on Meta to continuously innovate and maintain its market share.
Microsoft’s substantial investment in OpenAI and the integration of AI technologies into its products present another competitive front for Meta.
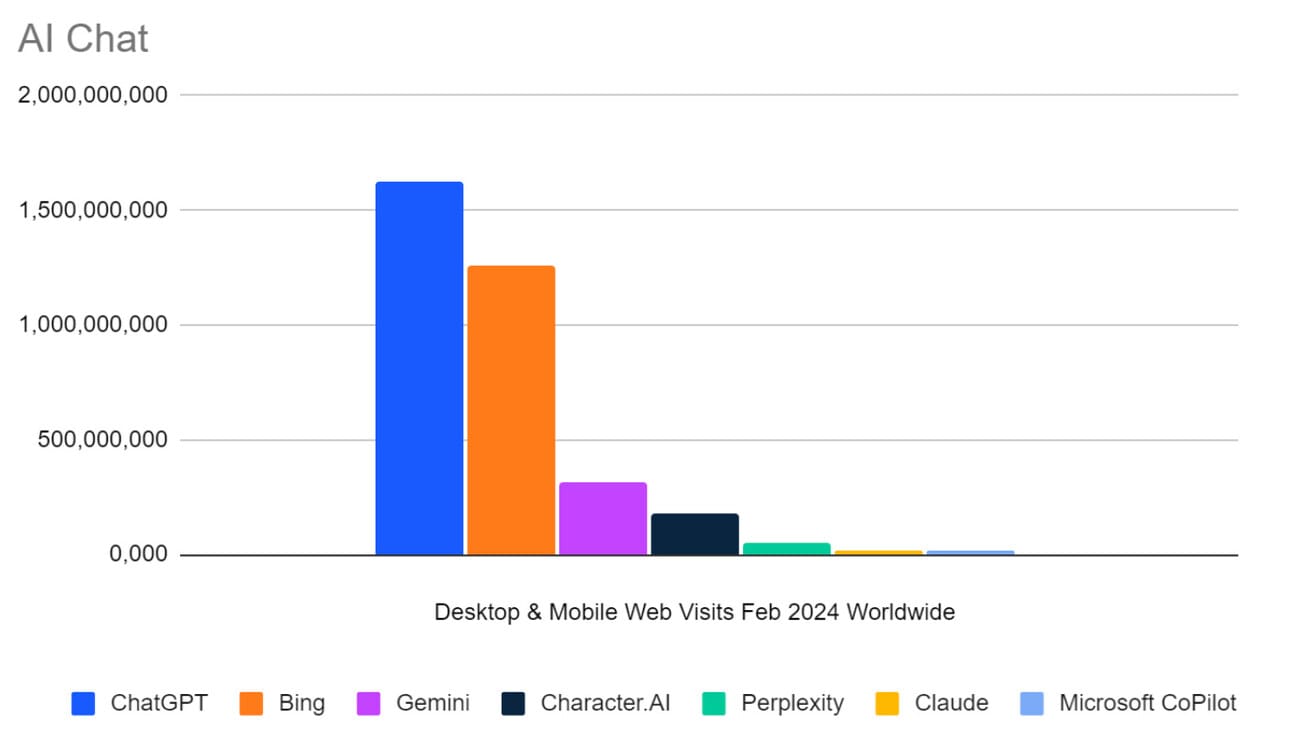
Apple’s entry into the AR/VR headset market with the Vision Pro poses a direct challenge to the Quest lineup. Apple’s emphasis on high-quality hardware and user experience drives Meta to enhance its own offerings, as seen in the improvements to Meta Quest 3 and the Meta Ray Ban Smart Glasses.
What do the consumers think
Meta’s AI advancements, particularly through its Llama models and integration across platforms have been celebrated by developers. The Llama 3 models improve upon Llama 2 significantly in terms of tasks like reasoning, code generation, and maintaining conversation context, and is powerful enough to compete with closed models from OpenAI and Anthropic.
The integration of Meta AI into platforms like Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Messenger, using Llama 3, has been very exciting and convenient for users. The chatbot can easily search for not just texts but also reels and videos and lets users ask questions about them. However, the Meta AI chatbot on the website has received mixed reviews. While it is extremely good at casual questions and image generation, it seems to just be doing a search for what you ask about and quoting from the top results. (Source)
Meta’s Ray-Ban Smart Glasses provides the hands-free experience and the practicality of having AI assistance readily available through voice commands but was limited in its functionalities and design options. But now, Meta is expanding the collection with the new Ray Ban Smart Glasses that have more designs, integrated Meta AI chatbot to which you can ask questions about what is infront of you or just about anything else. (Source)

Lastly, the Meta Quest 3 VR headset delivers an immersive experience with good value, yet it draws mixed reactions when compared to high-end competitors like Apple Vision Pro. While it is much cheaper than Vision Pro, its cumbersome controllers and slightly bulkier design contrast with the Vision Pro’s seamless and intuitive gesture controls. However better it gets in its capabilities and features, Meta Quest series will suffer from the typical problems of virtual reality heavy wearables.
Amazon
Brief Summary of the Business
Amazon’s sprawling empire encompasses e-commerce, cloud computing (AWS), digital streaming, and AI. While its online retail platform remains a cornerstone, Amazon’s diversification into various tech sectors, particularly leveraging AI, fuels its growth and dominance. Amazon boasts a market capitalization of approximately $1.8 trillion.
AI Integration and Innovation
AI permeates nearly every area of Amazon’s operations. Recommendation algorithms, powered by machine learning, personalized user experience on its e-commerce platform, driving sales and customer engagement. Warehouse automation utilizes AI-powered robots and predictive analytics to optimize logistics and delivery efficiency. Alexa, the company’s virtual assistant is also evolving with improved natural language understanding.
Beyond these core areas, Amazon invests heavily in AI research and development. Its cloud platform, AWS, offers a range of AI and machine learning services, empowering businesses to build their own intelligent applications. Furthermore, Amazon explores cutting-edge applications of AI in areas like drone delivery systems and autonomous driving technology through its subsidiary, Zoox. These advancements not only streamline Amazon’s internal processes but also have the potential to revolutionize entire industries.

Financial Performance
Amazon concluded 2023 with a stellar fourth quarter, exceeding market expectations and demonstrating robust financial performance. The company reported a significant 14% increase in net sales, reaching $170 billion, compared to $149.2 billion in the same quarter the previous year. This growth exceeded market expectations, with revenue forecasts initially set at $166 billion. The company’s earnings per share also impressed, achieving $1.00 per share, surpassing the anticipated $0.80 per share.
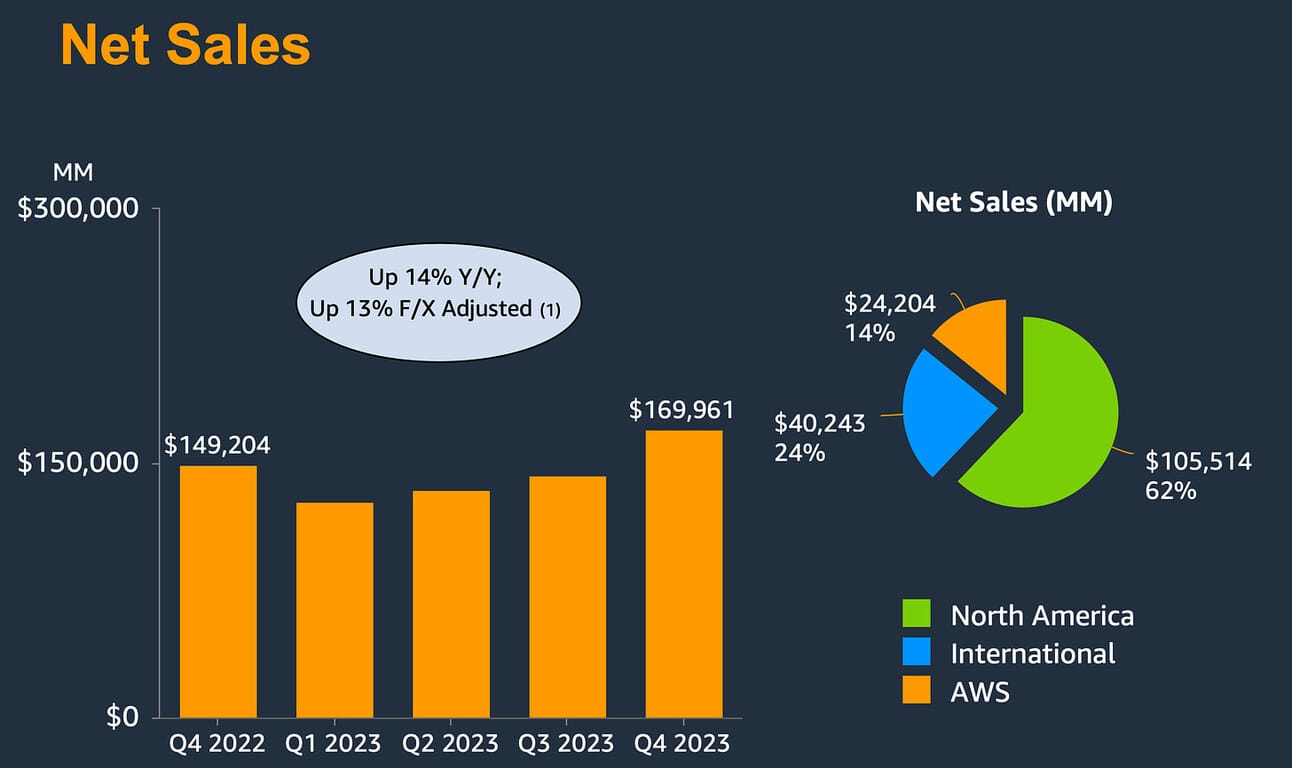
The increase in sales is indicative of Amazon’s continued expansion and resilience in the retail and cloud computing sectors. Notably, Amazon’s operating income saw a significant surge, increasing by 383% year-over-year to reach $13.2 billion. These figures highlight a strong end to the fiscal year, driven by high holiday season sales and efficient operational enhancements across its segments.
Amazon’s ongoing focus on expanding service offerings and prioritizing customer experience through AI integration and delivery speed improvements solidifies its position as a leader in the retail and technology sectors. (source)
Operational Efficiency
The company was laser-focused on operational efficiency and strategically leveraging AI across its various segments. The retail giant showcased impressive cost reductions, largely attributed to its regionalization efforts, which streamlined the fulfillment network and optimized inventory placement. This translated to faster delivery speeds and lower cost-to-serve, enabling Amazon to offer competitive pricing and a wider selection of products, ultimately enhancing the customer experience.
Beyond retail, Amazon’s cloud computing arm, AWS, exhibited robust performance, boasting accelerated revenue growth and a diminishing impact from customer cost-optimization efforts. The highlight, however, was the clear emphasis on generative AI.
AWS unveiled its comprehensive AI stack, encompassing custom-designed AI chips, the Bedrock platform for building and scaling foundation models, and innovative AI applications like Amazon CodeWhisperer. This strategic focus on AI, coupled with significant customer interest, positions AWS as a leader in the burgeoning generative AI landscape.

Amazon's commitment to AI extends beyond AWS, permeating its consumer-facing businesses. The launch of Rufus, an AI-powered shopping assistant, signifies a significant step towards revolutionizing product discovery and enhancing customer engagement on the retail platform. (Source)
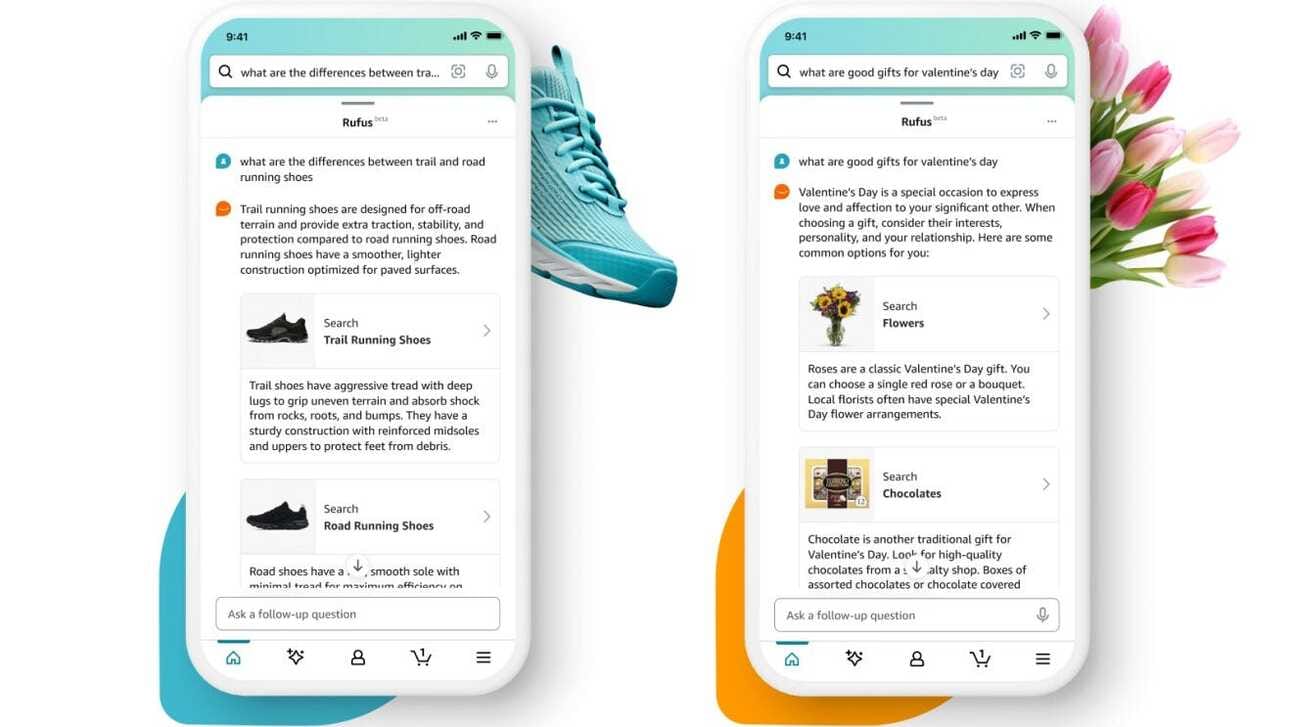
Key vendors
Amazon’s dominance in the cloud computing and AI landscape is significantly bolstered by its strategic partnerships with key technology providers. Nvidia stands out as a crucial collaborator, providing the high-performance GPUs essential for training and deploying large language models, the backbone of generative AI applications.
Beyond hardware, Amazon actively partners with leading AI companies like AI21 Labs, Cohere, Meta, and Stability AI. These collaborations enrich Amazon Bedrock, a managed service offering access to diverse foundational models through a single API. This approach streamlines AI integration for businesses, allowing them to leverage the latest AI advancements without the complexity of managing individual models and APIs.
One of the most notable partnerships of Amazon is its investment in the AI startup Anthropic, amounting to a staggering $4 billion. Since Anthropic is directly competing with major AI players like OpenAI and Google, this investment helps position the company at the forefront of generative AI development. Also, similar to Microsoft and OpenAI, this investment in Anthropic allows Amazon to gain access to Anthropic’s cutting-edge AI model called Claude. (The NYT)
Amazon’s network of partnerships extends beyond AI-specific technology, encompassing collaborations with established players like Intel, Micron, VMware, Cisco, and Samsung. These partnerships ensure robust and scalable infrastructure solutions, encompassing CPUs, memory, storage, networking, and cloud services, all of which are essential building blocks for supporting the demanding workloads associated with AI and machine learning applications.
Main competitors
AWS faces intense competition in the cloud computing market from major players like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). AWS has demonstrated strong incremental revenue growth, suggesting a competitive edge over its rivals. Additionally, AWS’s robust security features and proven track record could provide a significant advantage in the generative AI space, where data security is paramount.
AWS collaborates with various model providers, such as Anthropic, Cohere, Meta, and Stability AI, to offer customers a diverse range of options through its Bedrock service, recognizing the importance of choice in the rapidly evolving generative AI landscape. This collaborative approach allows AWS to cater to the diverse needs of its customers and maintain its position as a leader in the cloud computing and generative AI markets.
Further, Amazon’s CodeWhisperer coding companion tool competes with other offerings like GitHub Copilot. As generative AI continues to advance, Amazon acknowledges the need to provide developers with powerful tools to enhance productivity and streamline their workflows.
What do the consumers think?
Amazon's AI-powered services have garnered a mixed reception, with both praise and concerns from users. AI-generated review summaries are appreciated for their quick insights but raise questions about accuracy and potential bias. Similarly, Rufus, the AI shopping assistant, aids in specific queries but struggles with broader tasks, leading to doubts about transparency and effectiveness. (Signalytics, Techcrunch)
Amazon Bedrock on the other hand is lauded for its user-friendliness and quick deployment of generative AI applications, while SageMaker stands out for its comprehensive support and customization options throughout the machine learning lifecycle. Both tools are valued for their robust capabilities and security features.
Amazon CodeWhisperer has received a polarized response. While some said it enhanced productivity with real-time contextual coding suggestions, others focused on issues like suggestion quality and stability. They say it is “not worth it” and is only a minor improvement over IDE-based auto-completions, but not very useful for generating complex code. (Codeium)
Conclusion
The Magnificent 7, with their aggressive AI integration and innovation, undoubtedly shape the trajectory of the entire market. But the outlook for near-term is very uncertain. The potential of a market correction looms large, driven by high valuations and an ever-changing economic backdrop marked by inflationary pressures and geopolitical tensions. The AI sector, while promising, is not immune to these broader market forces and thus, demands cautious optimism.
The rapid pace of advancements in areas like generative AI, natural language processing, and computer vision opens up new possibilities and will lead the future of not just the tech but all industries! But it is also important to keep looking for market signals to take the next course of action.
Diversification should play a critical role in mitigating risks associated with this short-term volatility. By spreading investments across a variety of sectors and not just heavily investing in tech, you can shield yourselves from tech-specific downturns and capitalize on a wider breadth.
Maintaining a long-term perspective is essential, especially in a sector where the innovations today take some time to fruition. View your investments in AI-bent companies with an eye toward enduring growth and potential, rather than short-term gains.
AI’s transformative potential extends far beyond algorithms and models; it hinges on real-world applications and tangible value creation. Keep a watchful eye on how these technological advancements translate into practical solutions and market adoption, while being informed and agile about the broad market. And you should be set!
That’s all for today 👋
See you next week with another interesting AI deep dive, where we’ll explore fascinating aspects of the latest AI breakthroughs in depth. Can’t wait to share more insightful discussions and discoveries in the world of AI with you.
Click on the subscribe button and be part of the future, today!
📣 Spread the Word: Think your friends and colleagues should be in the know? Click the ‘Share’ button and let them join this exciting adventure into the world of AI. Sharing knowledge is the first step towards innovation!
🔗 Stay Connected: Follow us for updates, sneak peeks, and more. Your journey into the future of AI starts here!